Finding the Throughline in Multi-Hazard Planning
Not so very long ago, certainly within the memory of most millennials, all that the Bay Area really had to fear from Mother Nature was the occasional earthquake. Terrifying when they occurred, certainly, but blessedly infrequent. The rest of the time we could all look smugly to the East, where our fellow citizens regularly contended with blizzards, tornados, hurricanes, and more.
Not anymore. Thanks to the changing climate, the Bay Area now faces increasingly frequent threats from flooding, heat, wildfire and smoke. As the hazards multiply, communities, local governments, and agencies are searching for ways to address them more holistically.
“The ways you build resilience is oftentimes similar for different types of hazards,” says Matt Wolff, of San Francisco Department of Health’s Climate and Health Program. Wolff co-leads the city’s Heat and Air Quality Resilience Project, which brings together public, private, community and academic stakeholders to develop extreme heat and wildfire smoke resilience strategies. The incidence of both hazards is increasing, and Wolff notes that the strategies for dealing with one are often effective for the other.
“It’s about protecting people from outside exposures,” he says, “focusing on building envelopes, for example, and making sure they protect against both heat and smoke. We are looking at how many co-benefits there are to any particular solution.”
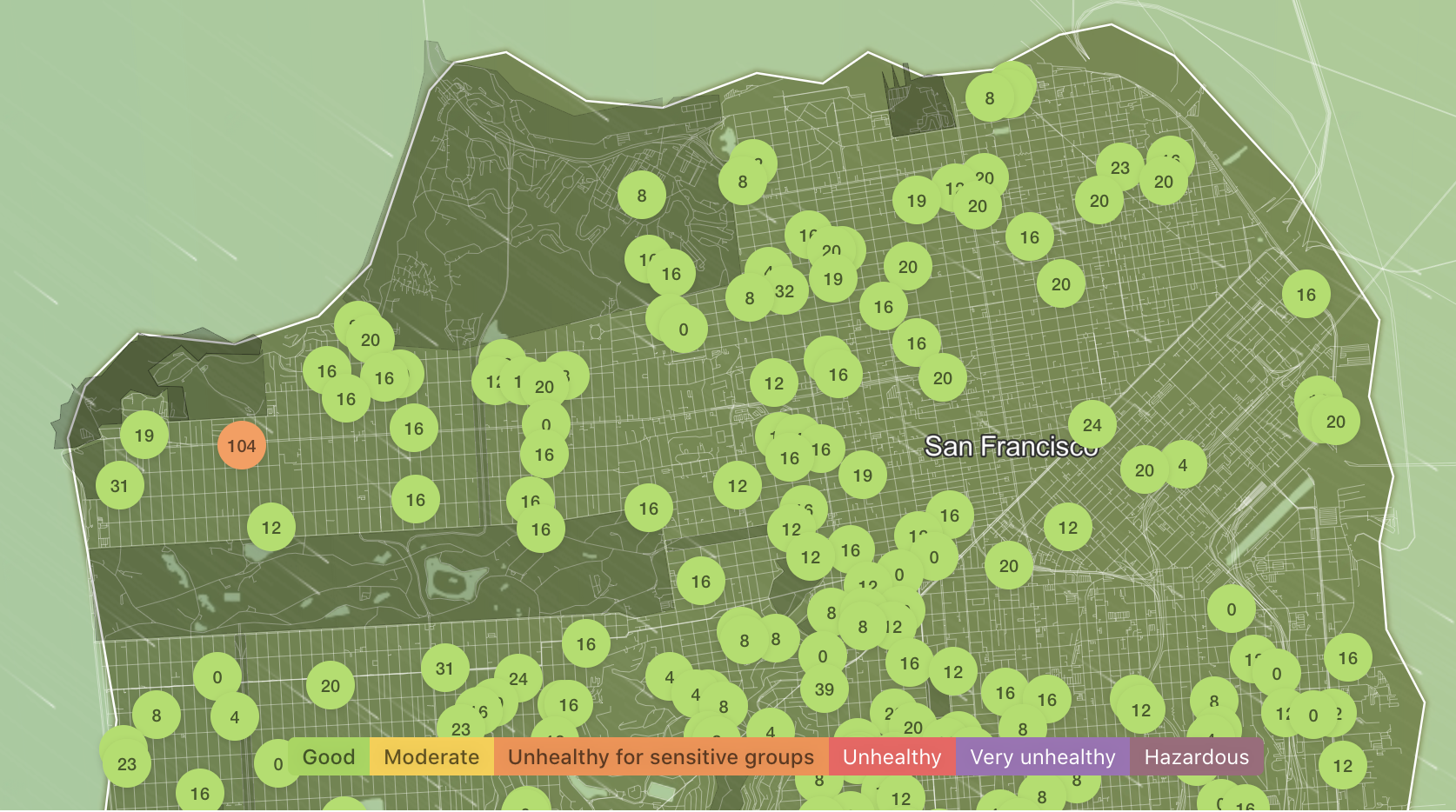
IQ air quality index for San Francisco on October day.
“If you just look at each hazard one at a time, you miss a lot of opportunities,” says Matt Chadsey of Nonlinear Ventures, who consulted on a new report for the Bay Area Regional Collaborative that analyzes the climate adaptation activities of its member agencies. “The problems have been looked at in silos to some degree—coastal flooding issues and sea level rise separate from wildfire separate from air quality, and so forth. One of the things that’s pretty clear is that the more we can look at things holistically, from a community perspective, the more we increase the likelihood of collaboration, of innovative thinking, potentially more funding coming in.
The BARC report is a first step towards the development of a regional multi-hazard adaptation plan and a technical assistance program, according to BARC’s Allison Brooks. In addition to mapping the BARC member agencies’ existing adaptation efforts, as well as the relationships and resources that support them, and fitting them into the bigger picture of Bay Area adaptation, the report identifies gaps and challenges in the region’s approach to adaptation. It also assesses the technical assistance available to stakeholders, and explores opportunities for improving it.
Multihazard adaptation means more than just preparing for disasters, says Chadsey. “It’s taking a step back and looking at the whole, both the natural and the social system of the community and really addressing everything together,” he says . “It’s really trying to understand how equity and diversity play, and how local jobs and the local economy play in the actual risk mitigation activities, because there are a lot of opportunities to do more to make a healthier community overall.”
BARC is a funder of KneeDeep Times.
Other Recent Posts
Tools Tweak Beaver Dams
After witnessing fire disasters in neighboring counties, Marin formed a unique fire prevention authority and taxpayers funded it. Thirty projects and three years later, the county is clearer of undergrowth.
Reforming Rules to Speed Adaptation
Bay Conservation and Development Commission to vote early this year on amendments designed to expedite approval of climate projects.
Warner Chabot Shifts Gears
After 11 years at the helm of the Bay Area’s leading science institute, its leader moves back into the zone of policy influence.
Is Brooklyn Basin Emblematic of Regional Development Vision?
The 64-acre waterfront development adds thousands of new housing units to one of the world’s most expensive places, but questions remain about its future.
Coordinate or Fall Short: The New Normal
Public officials and nonprofits say teaming up and pooling resources are vital strategies for success in a climate-changed world.
Pleasant Hill Gets Sustainable Street Improvements
An intersection redesign with safer bike lanes earned a national Complete Streets award, while sparking mixed reactions from drivers.
Six Months on the Community Reporting Beat
The magazine worked with four journalists in training from community colleges, and began building a stronger network in under covered communities.
Rio Vista Residents Talk Health and Air Quality
A Sustainable Solano community meeting dug into how gas wells, traffic, and other pollution sources affect local air and public health.
New Year Immerses Concord Residents in Flood Preparations
In Concord, winter rains and flood risks are pushed residents to prepare with sandbags, shifted commutes, and creek monitoring.
What You Need to Know About Artificial Turf
As the World Cup comes to the Bay Area, artificial turf is facing renewed scrutiny. Is it safe for players and the environment?