Who’s on First at the SF Seawall?
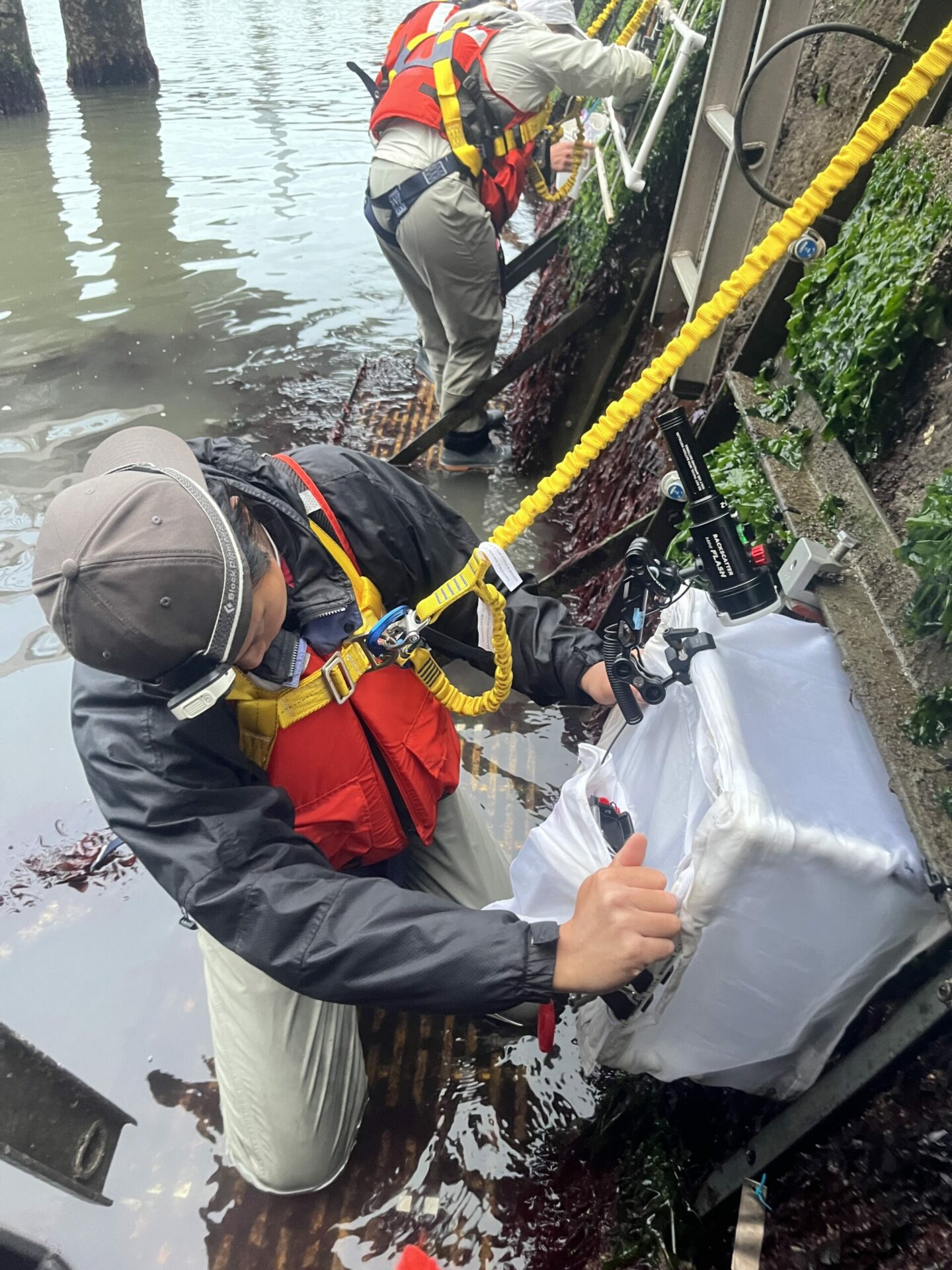
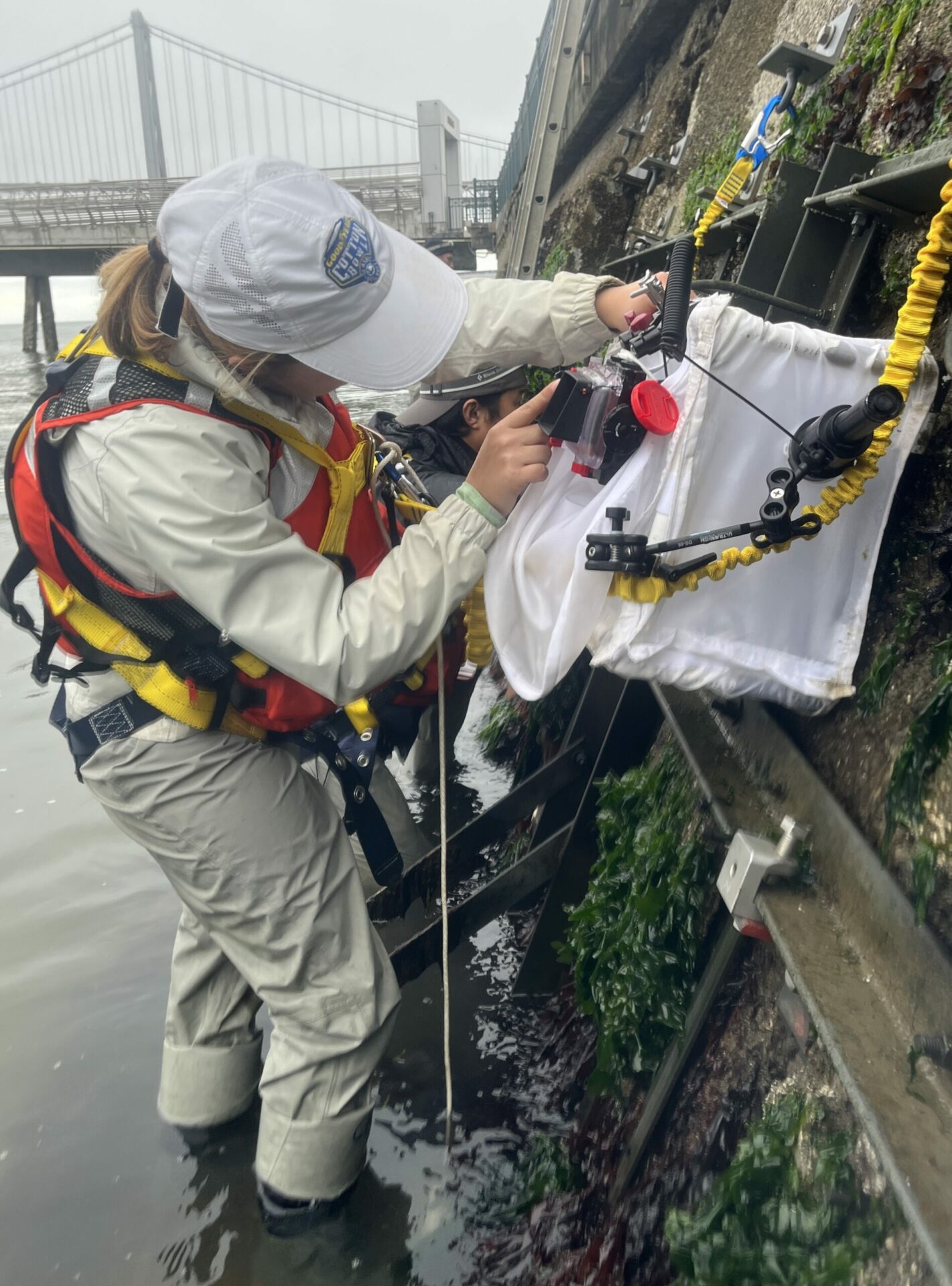
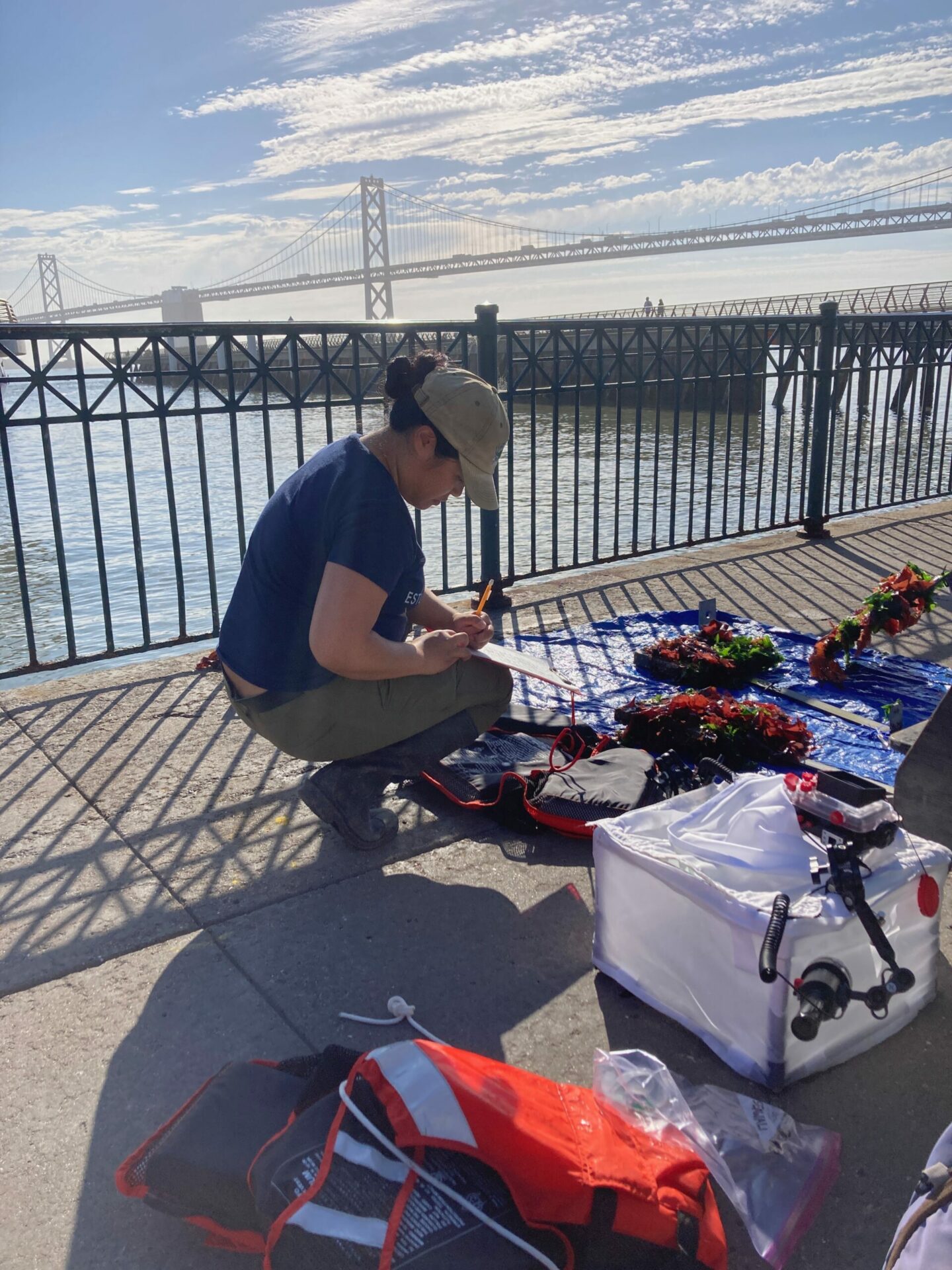
Ecologist Andrew Chang and biological tech Jessika De Jesus sample new seawall tiles this August. Photo: Corryn Knapp, SERC/SFSU.
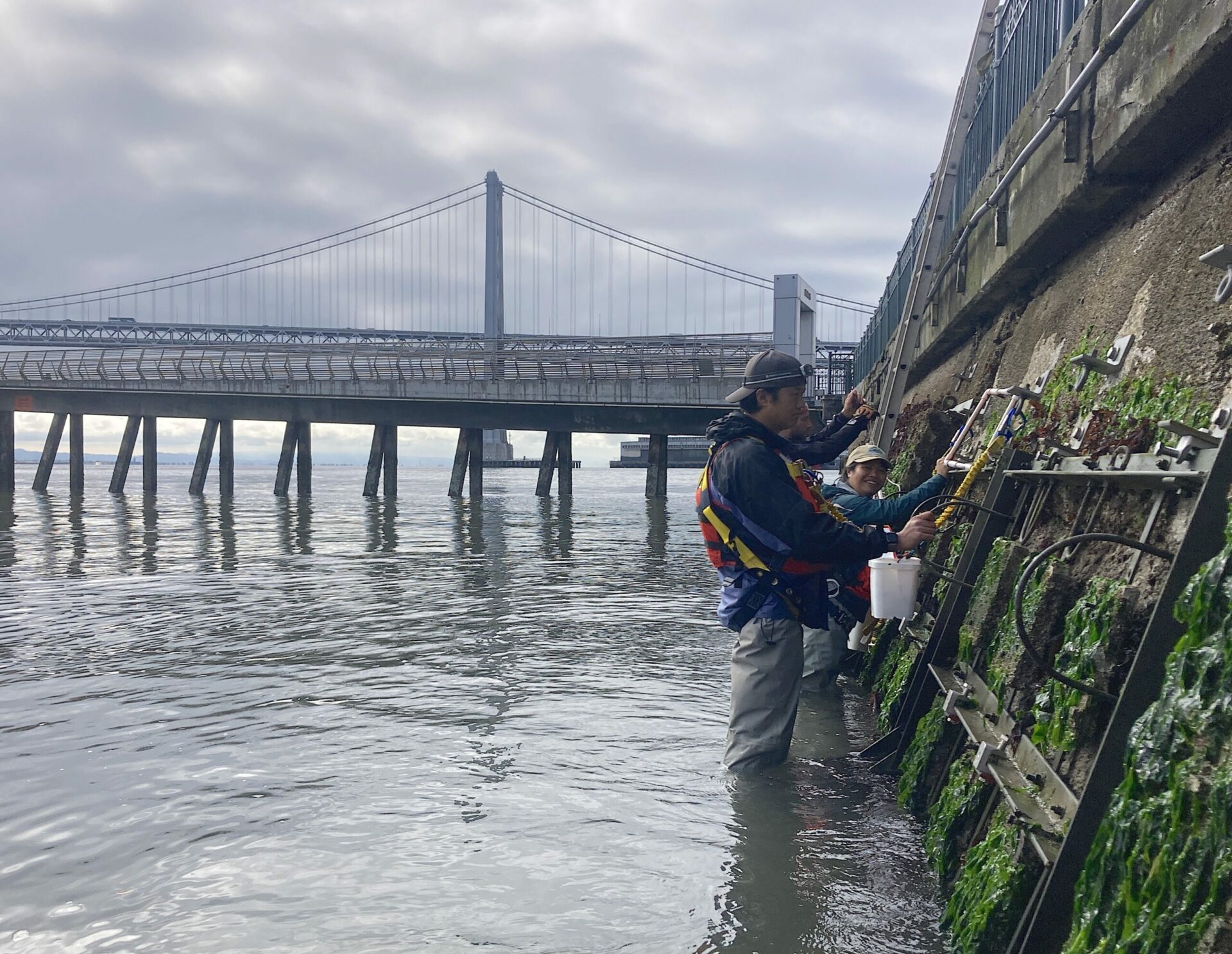
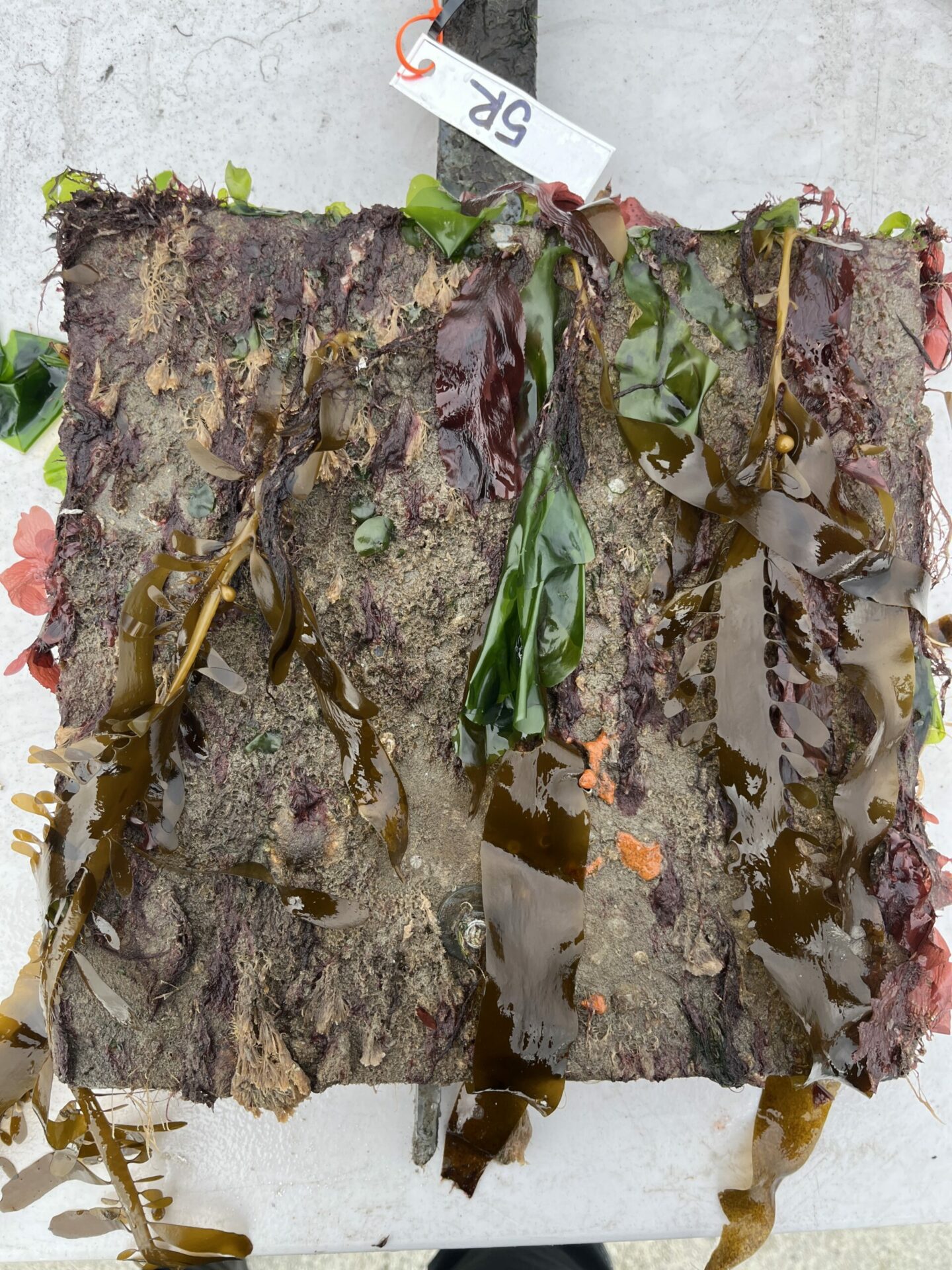
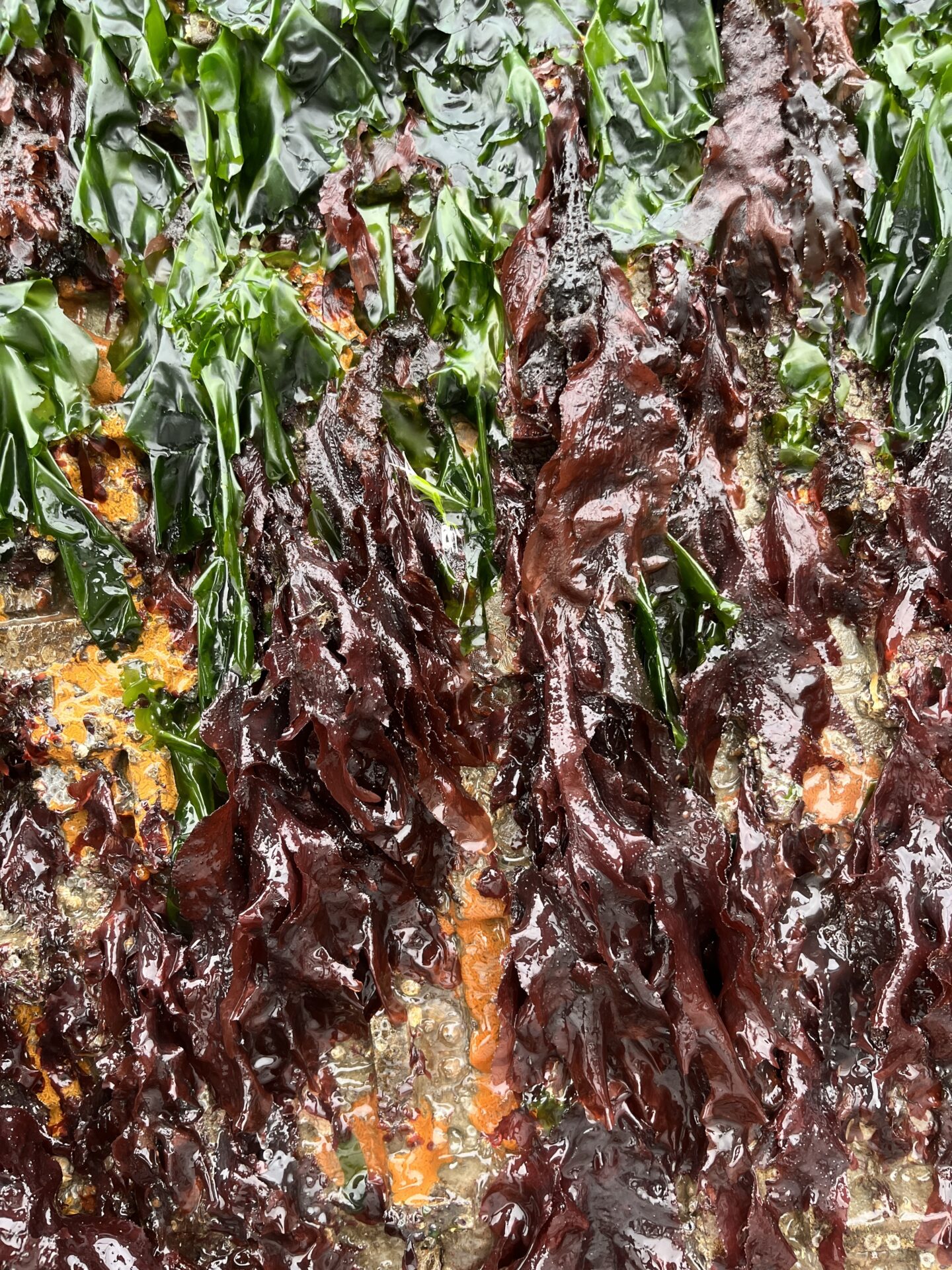
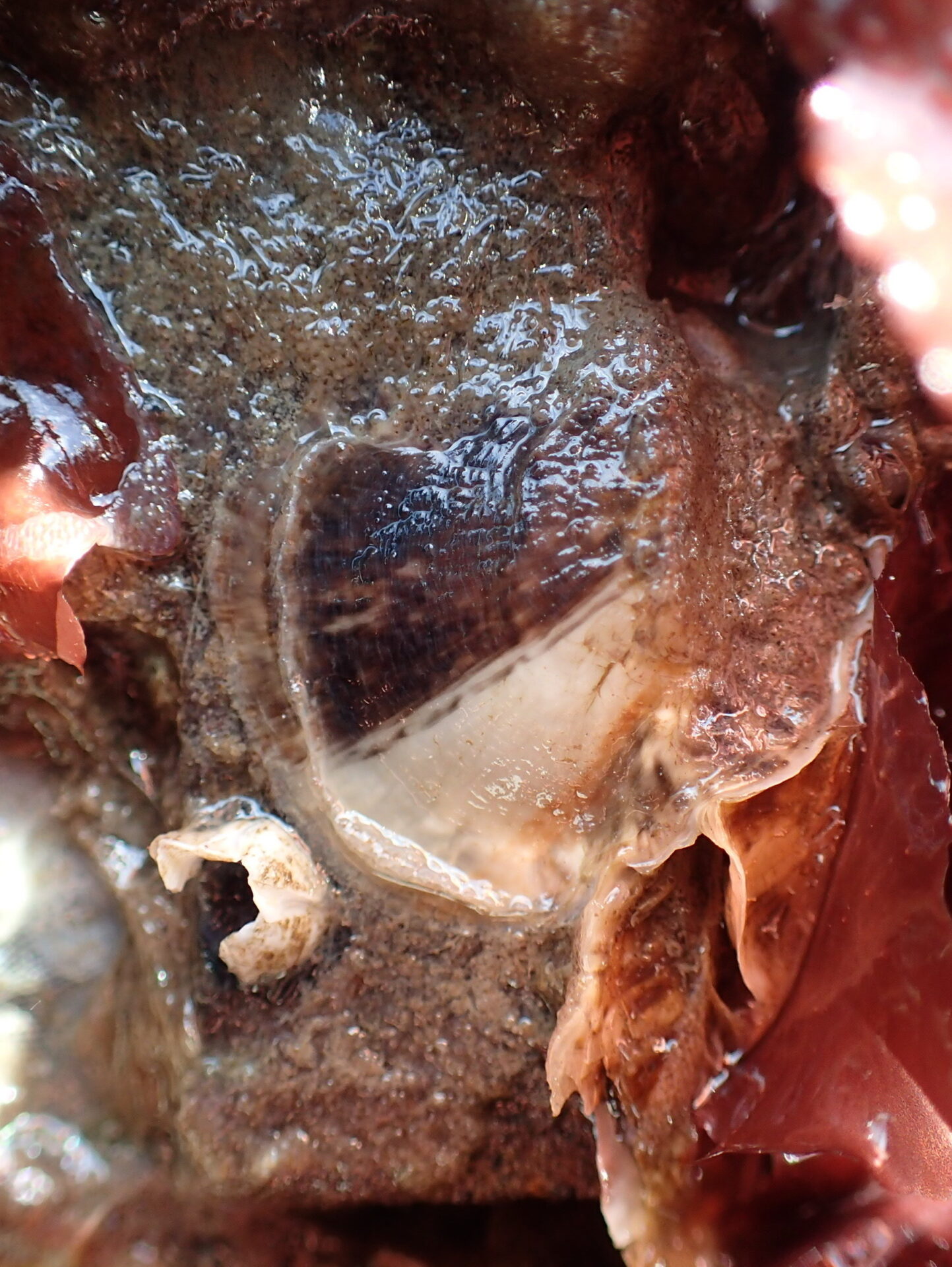
Ten months after the Port of San Francisco lowered 288 experimental tiles into the water, these bio-friendly seawall surfaces are already crawling with crabs and covered in kelp. This August, researchers are finally getting a good look at all the tile types in their experiment, which range from large to small, and from bumpy to smooth, and which were hung from the waterfront at three different locations and tidal elevations in October 2022.
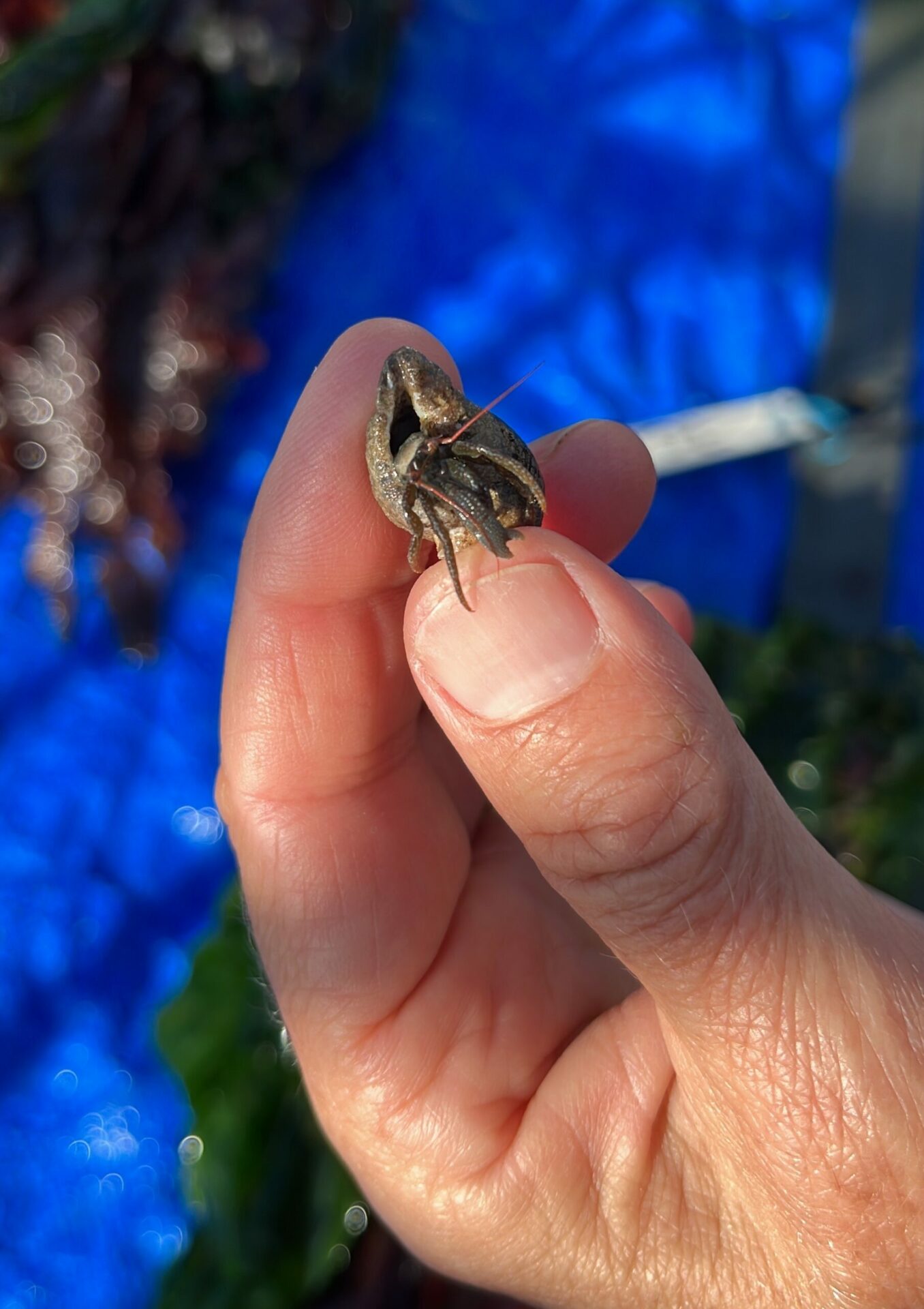
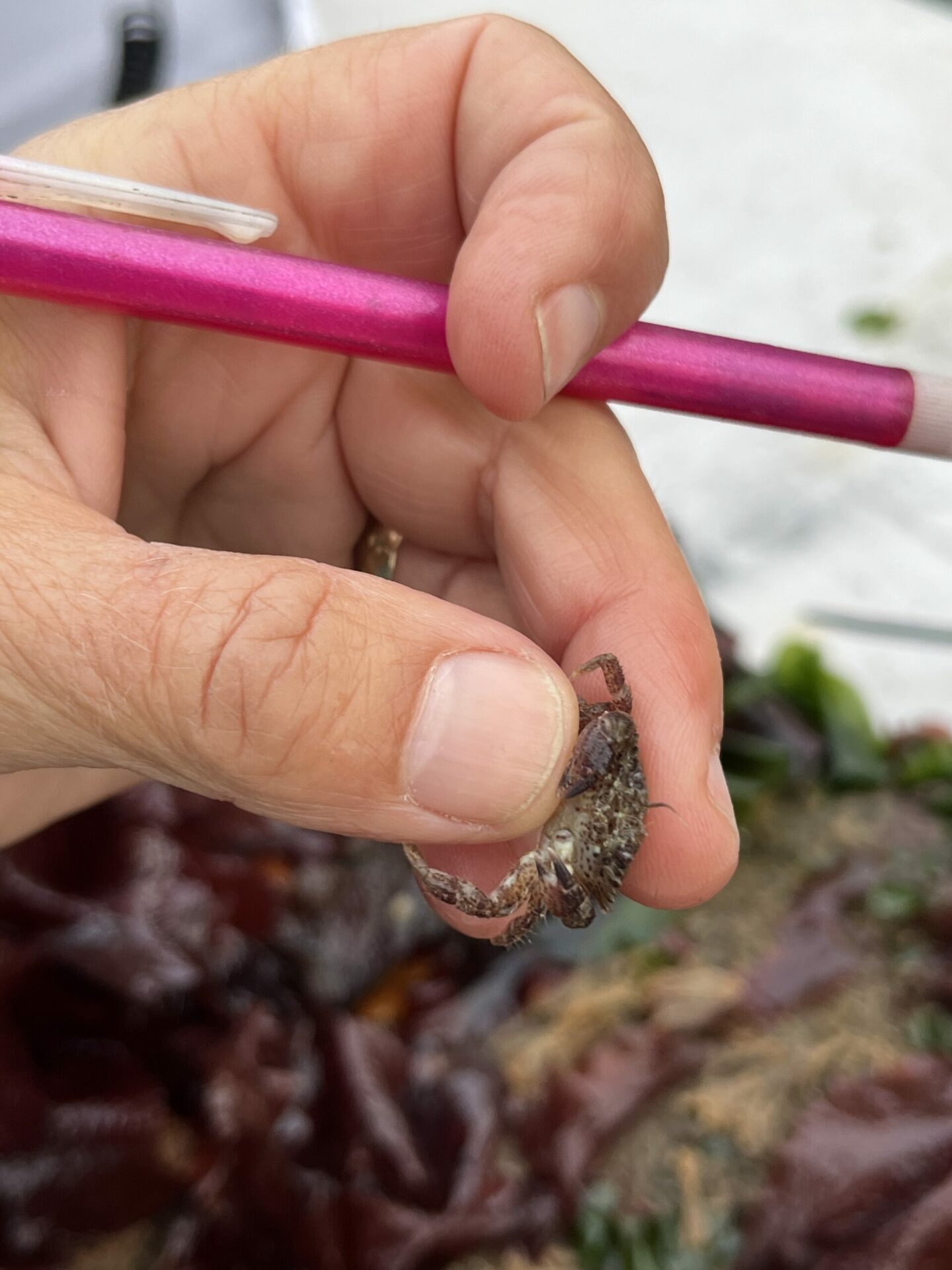
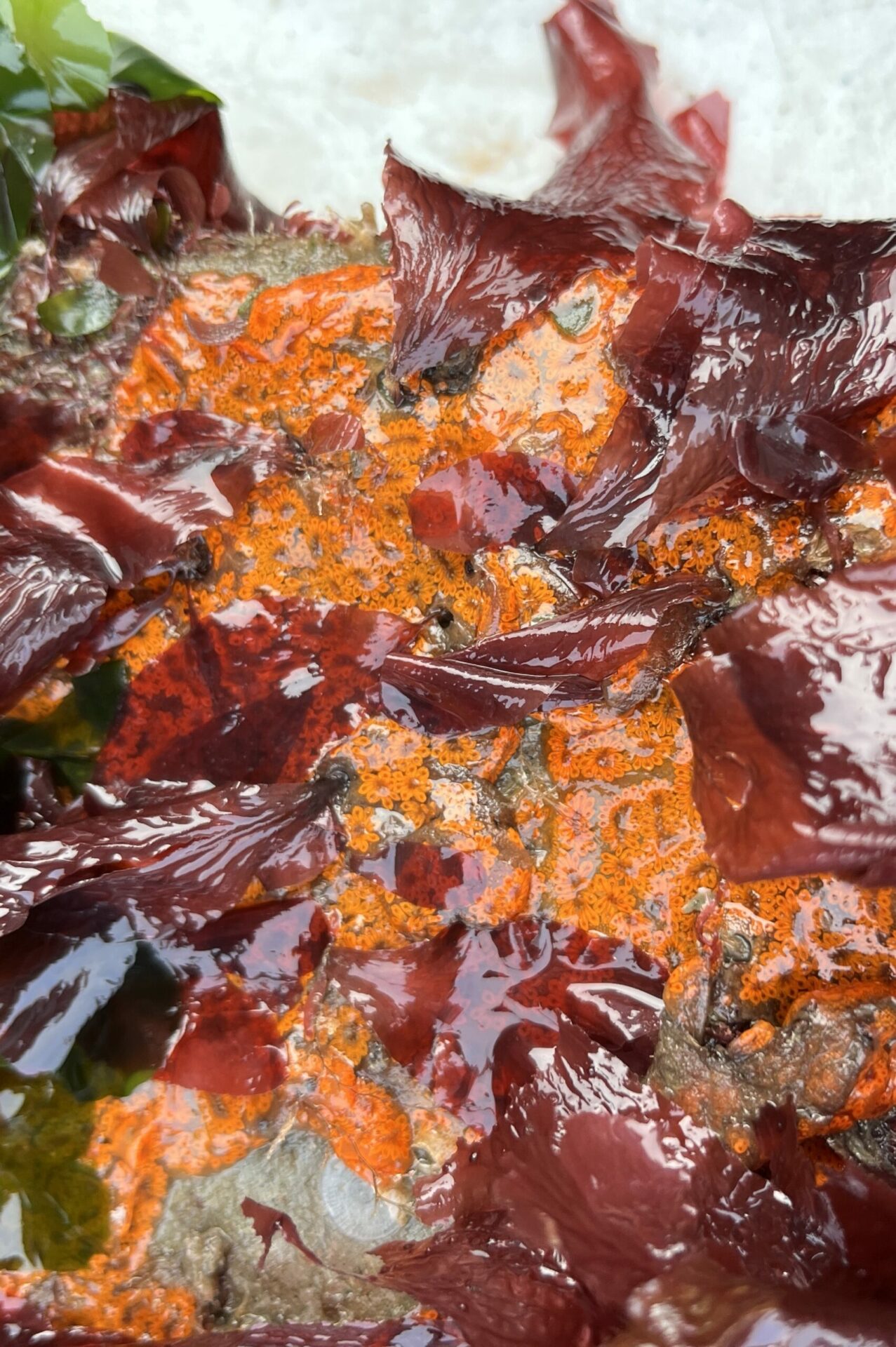
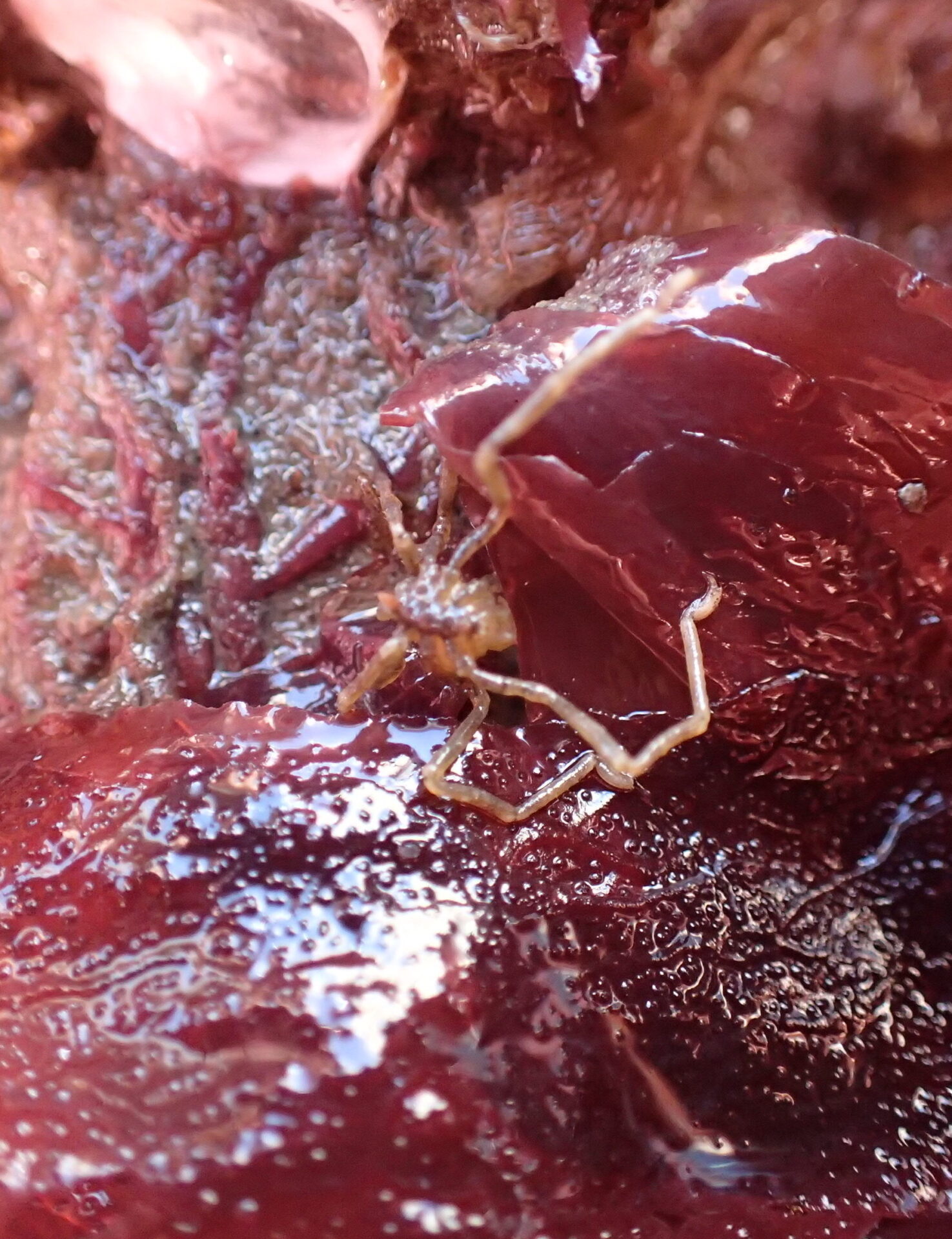
“We saw a ton of native species and a few non-native ones,” says ecologist Andrew Chang with the Smithsonian Environmental Research Center, launching into a list including chitons, limpets, native oysters, Mastocarpus and Laminaria (red and brown algae ), hermit crabs … “We saw mobile critters settling on the tiles and making a home for themselves or migrating from the adjoining seawall, where there’s a more mature community.”
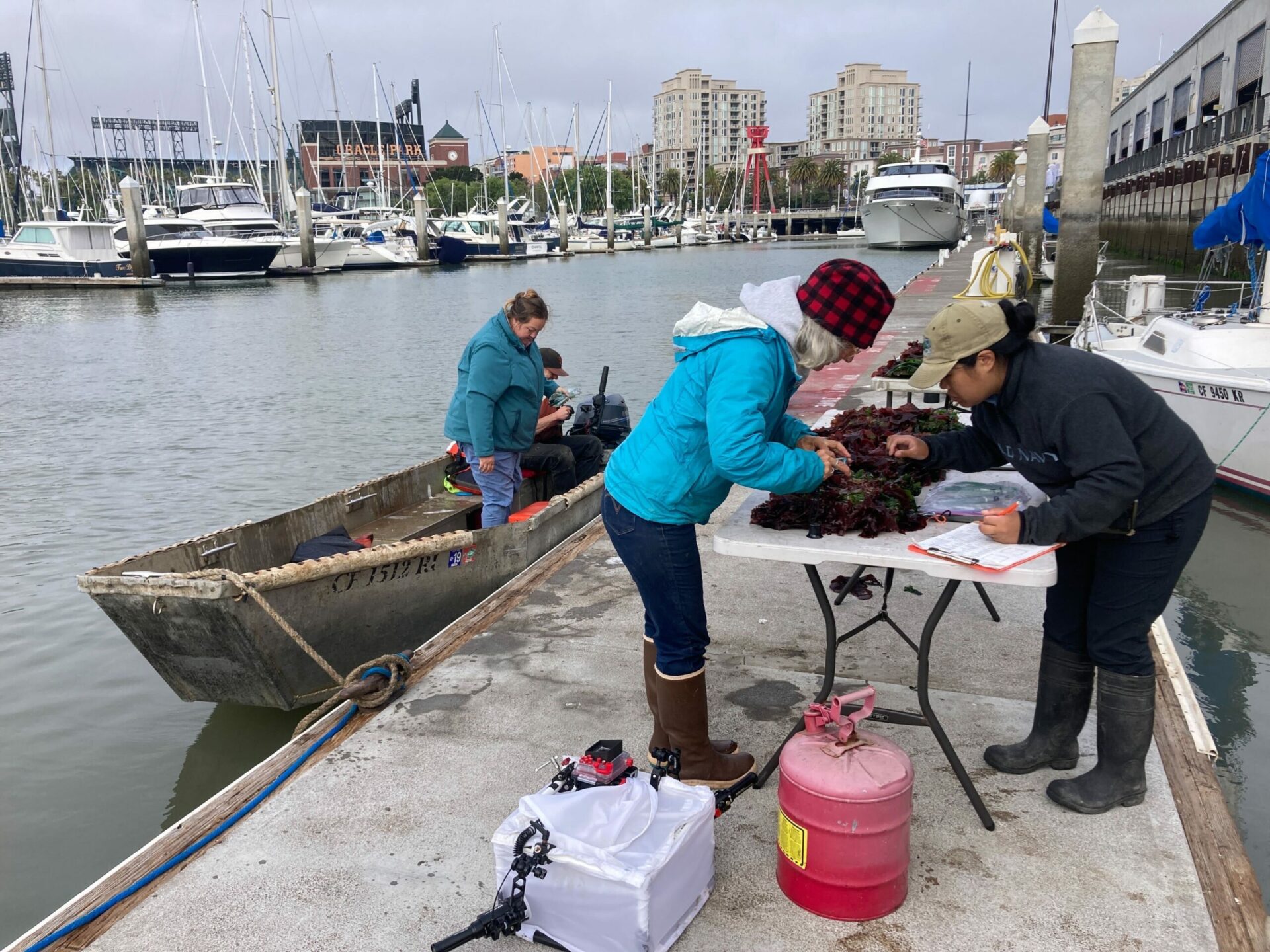
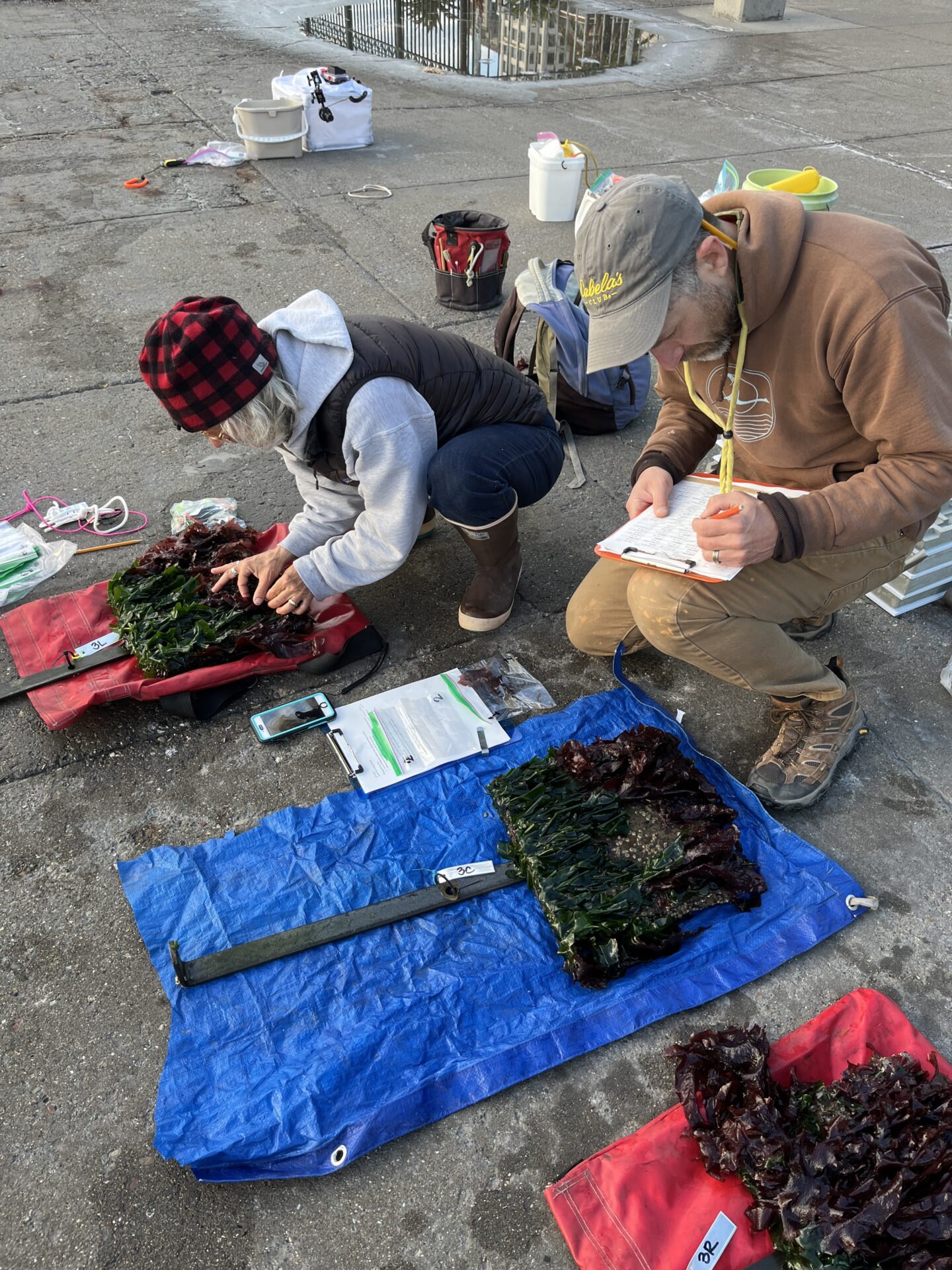
Scientist Chela Zabin and tech Jessika De Jesus scrutinize lower elevation tiles pulled up by port divers at South Beach Harbor marina site, before returning them to the water. Photo: Corryn Knapp, SERC/SFSU.
As reported in KneeDeep’s October 2022 story about the experiment, scientists and the port hope to ensure that the massive seawall rebuild required to adapt to rising sea levels along the San Francisco waterfront includes some habitats friendly to native intertidal and subtidal species. The experiment called for a two-year monitoring period, during which the science team would pay regular visits to the three sites so they could photograph and ID species on the tiles. Access to the tiles in the deepest water was to be provided by moveable frames, platforms and other installation innovations created by Port staff.
But this past March, during a brief lull in the wave-lashing from winter storms, port divers and the science team discovered quite a bit of damage to frames and some broken or missing tiles. Then the severe weather returned. “We couldn’t get anywhere near a complete check-in done, it wasn’t safe enough to get more than the barest of impressions,” says Chang.
This August’s push is more promising already. Though the frames and platforms were still unsafe at the South Beach Marina site, the team was able to view most of the tiles at the Agricultural Building (near the Ferry terminal) and Pier 45. “This site is much closer to the Golden Gate, so we saw more open-coast species like feather boa kelp that thrive in wave-exposed environments,” says Chang.
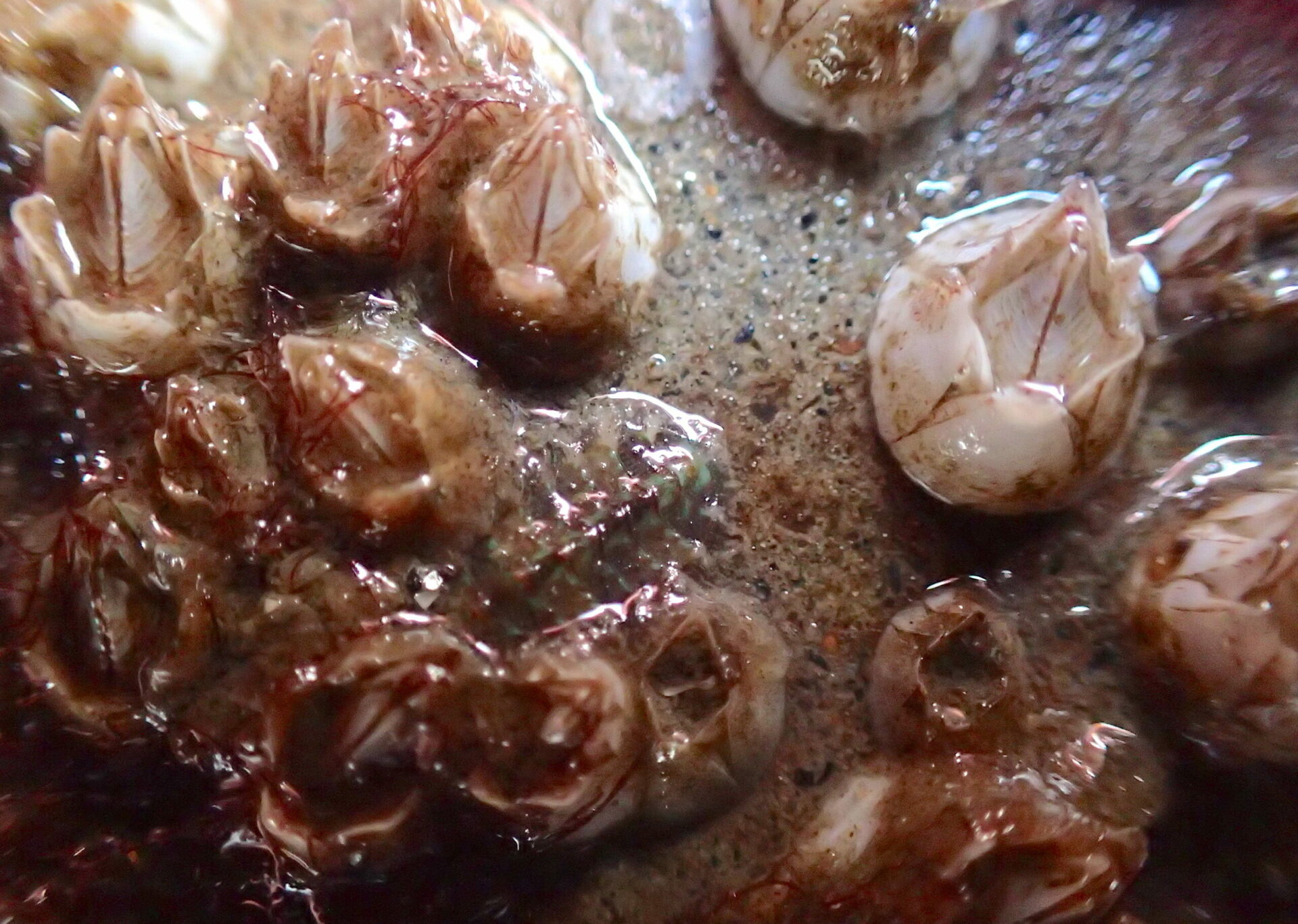
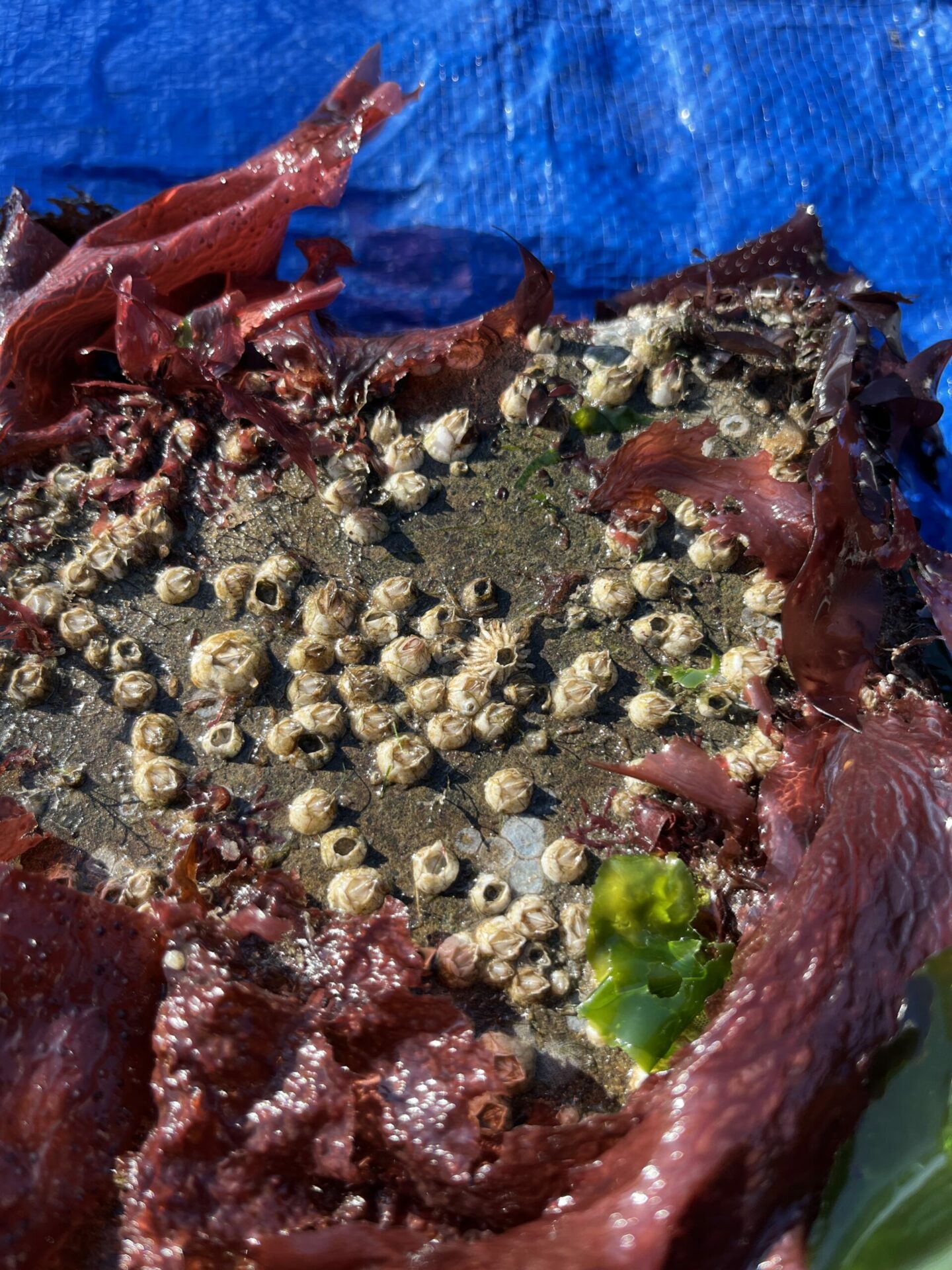
Native chitons and barnacles found at the Agricultural Building site at low tide. Photo: Chela Zabin, SERC.
Since the monitoring work is ongoing, such observations are just preliminary. But Chang was clearly excited to be putting on his drysuit, clipping into a harness, and hanging off a pier with a camera lightbox in one hand and a clipboard in the other to start filling in his data sheets. “After all the time spent working with a large group of people to design this experiment, and time talking about all the stuff that needed to happen to put it all in place, it’s great to get a good look at the tiles in action,” says Chang.
More definitive results should be ready by the end of the year. But one important take home, as Chang’s co-lead for the project Chela Zabin put it, was evident: “At first glance natives dominated.”
Other Recent Posts
Adaptation Atlas
Thirty places to focus on nature-based adaptation around the Bay’s 400-mile shoreline.
Agroecology Commons Weathers a Weird Winter and Political Storms
A year after our first Agroecology Commons visit, the El Sobrante farm has a new greenhouse foundation, thriving farmer training program, and some unexpected wildlife.
Finding Community at the Bay Area Climate Literacy Exchange
A third of our food supply goes to waste, and Bay Area students are learning how to fix it one school cafeteria at a time.
Easy Spring Vegetables for Small Gardens
Snap peas and Tokyo turnips are hardy, cool-season vegetables well-suited to Bay Area gardens. Here’s how to grow and cook them.
At Canticle Farm, Food and Community Are Prayer for a Better World
On a residential street in East Oakland’s Fruitvale neighborhood, a front yard becomes a food distribution network every Friday.
What Do Teens Think is Healthy Food?
Student reporting fellow Sachi Bansal asks three high school seniors in Fairfield about how they define healthy food, and what they think of the new food pyramid.
En Canticle Farm, la comida y la comunidad son las oraciones para un mundo mejor
Canticle Farm está reinventando el concepto de vecindario a través de la tierra compartida, la comida gratuita y la acogida radical.
En la granja agroecológica Agroecology Commons, las nutrias han vuelto
Un año tras nuestra primera visita a Agroecology Commons, la granja en El Sobrante tiene una nueva base para un invernadero, un próspero programa de entrenamiento para agricultores y una fauna inesperada.
Verduras de primavera fáciles de cultivar en jardines pequeños
Los chícharos dulces y los nabos japoneses son verduras resistentes al frío, ideales para los jardines del Área de la Bahía. Aquí te explicamos cómo cultivarlos y cocinarlos.
Entrenar futuros agricultores para que cultiven más que solo alimentos
En un colectivo del Área de la Bahía para agricultores BIPOC y queer, Brooke Porter y Alexa Levy luchan por construir, desde la tierra, un sistema alimentario inclusivo.