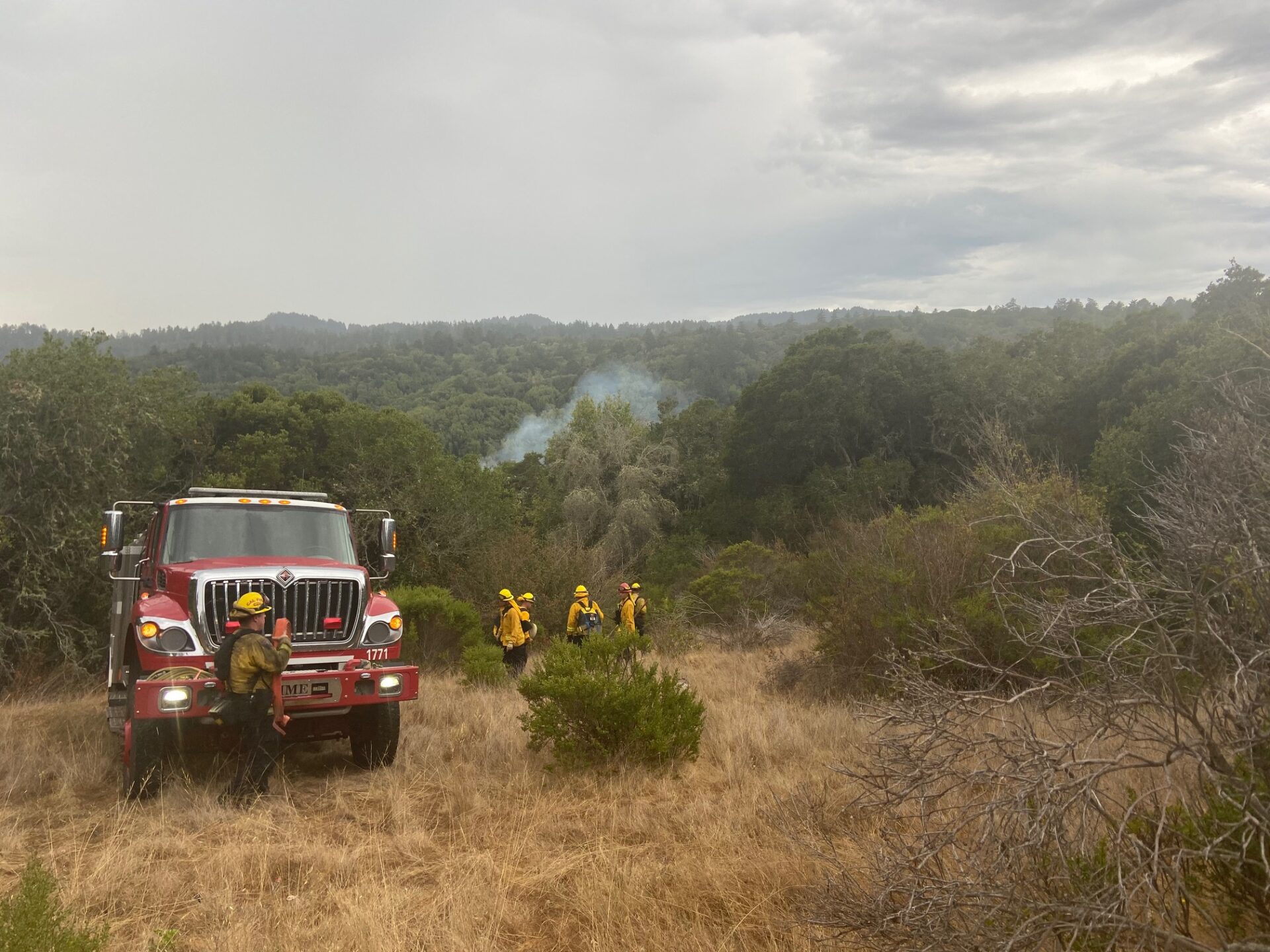
Chasing the Fireline
In a changing world, maps become outdated. Those depicting the Aral Sea as a vast blue ink stain in central Asia are years behind the curve, for much of the giant lake has been depleted by agricultural diversions and desertification. Many maps where lush equatorial green represents tropical rainforest fail to reflect deforestation.
In California, climate change has pushed another sort of map toward obsolescence. Prolonged droughts and increasingly severe heat waves have amplified the state’s wildfire season, rendering a collection of wildfire hazard zone maps, published 15 years ago by state fire officials and used to guide development and planning processes, out of date.
Jim McDougald, staff chief for the California Department of Forestry and Fire Protection (Cal Fire)’s community wildfire preparedness and mitigation program, says that wind-driven wildfires in fall and winter have seen an uptick in the past five to ten years, especially in Napa and Sonoma counties.
Now, Cal Fire is making changes to the agency’s Fire Hazard Severity Zone maps to more accurately portray the most flammable regions of the state.
“The new maps will be a lot more accurate to the weather that we’re now experiencing in California,” McDougald says.
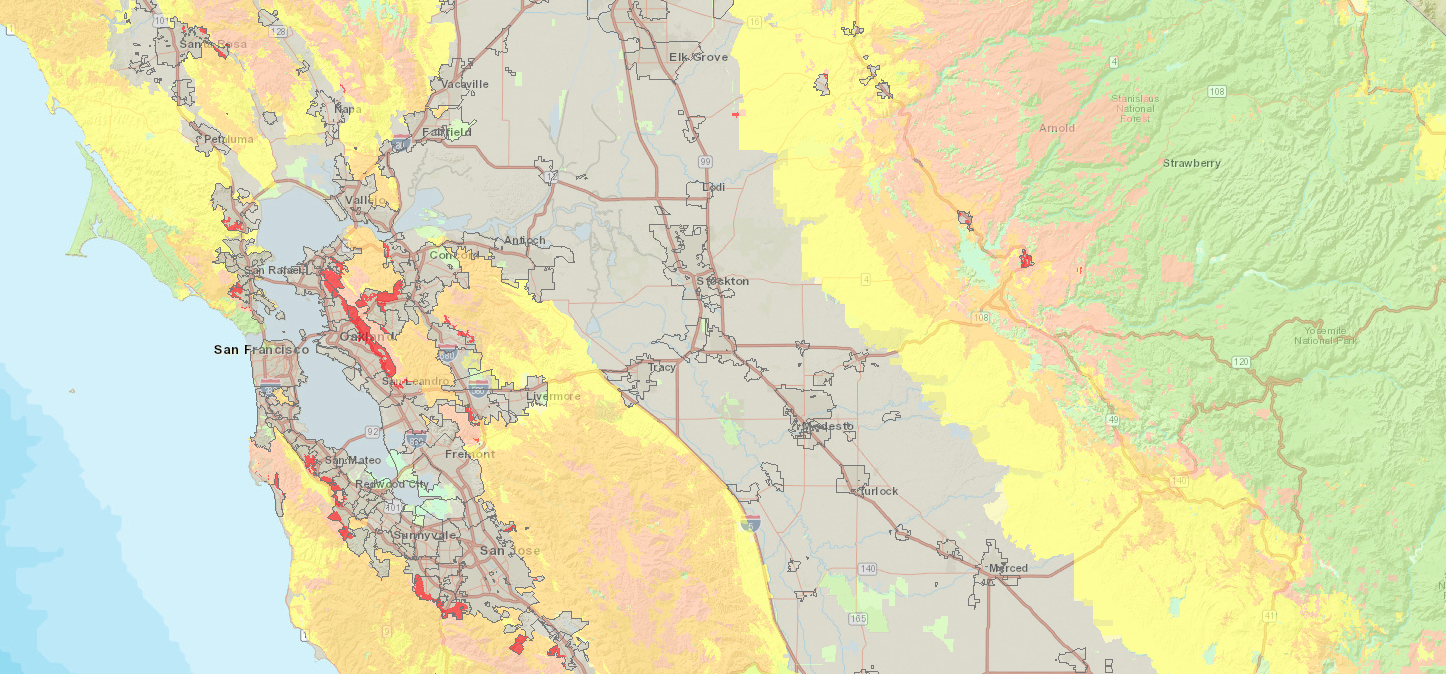
The maps, viewable online and last updated in 2007, use color coding to delineate regions at high resolution based on fire hazard level. Revisions, McDougald says, are being submitted to local Cal Fire units for review and necessary tweaking this summer. This fall, the agency will present its final maps.
According to the 2007 maps, one of the most fire-prone areas in the Bay Area is the East Bay hills, where a north-south swath of bright red and salmon pink — color code for “very high” hazard in, respectively, locally managed areas and lands managed by Cal Fire — runs from Hayward to north Richmond. Berkeley, El Cerrito, Piedmont, and Oakland each contain high-danger zones. On the San Francisco peninsula, a similar hazard band runs from Woodside almost to Burlingame, spilling westward over the ridge and down to the San Mateo coast. San Bruno Mountain is charted as a moderate hazard area, while vast swaths of the North Bay, from Santa Rosa to Lake Berryessa and northward through Lake and Mendocino counties, are rated as very high. Western Sonoma County is a notch lower.
Other Recent Posts
Reforming Rules to Speed Adaptation
Bay Conservation and Development Commission to vote early this year on amendments designed to expedite approval of climate projects.
Warner Chabot Shifts Gears
After 11 years at the helm of the Bay Area’s leading science institute, its leader moves back into the zone of policy influence.
Is Brooklyn Basin Emblematic of Regional Development Vision?
The 64-acre waterfront development adds thousands of new housing units to one of the world’s most expensive places, but questions remain about its future.
Coordinate or Fall Short: The New Normal
Public officials and nonprofits say teaming up and pooling resources are vital strategies for success in a climate-changed world.
Pleasant Hill Gets Sustainable Street Improvements
An intersection redesign with safer bike lanes earned a national Complete Streets award, while sparking mixed reactions from drivers.
Six Months on the Community Reporting Beat
The magazine worked with four journalists in training from community colleges, and began building a stronger network in under covered communities.
Rio Vista Residents Talk Health and Air Quality
A Sustainable Solano community meeting dug into how gas wells, traffic, and other pollution sources affect local air and public health.
New Year Immerses Concord Residents in Flood Preparations
In Concord, winter rains and flood risks are pushed residents to prepare with sandbags, shifted commutes, and creek monitoring.
What You Need to Know About Artificial Turf
As the World Cup comes to the Bay Area, artificial turf is facing renewed scrutiny. Is it safe for players and the environment?
Threatened by Trump’s Policies, GreenLatinos Refuses to Back Down
National nonprofit GreenLatinos is advancing environmental equity and climate action amid immigration enforcement and policy rollbacks.
Fire hazard severity zone map from 2007. Officials point out that “hazard” is not the same thing as “risk,” which is associated more with human behavior (the material a home is built of, how close a structure is to the edge of a forest, etc). Hazard encapsulates greater environmental aspects, like the forest itself and elements of climate, such as the notoriously fire-friendly Santa Ana and Diablo winds.
Exactly why late-fall and winter wildfires are becoming more severe is explained by several factors, says Sasha Gershunov, a research meteorologist at the Scripps Institution of Oceanography. He says data on wind patterns do not indicate significant changes in strength, frequency or seasonality. Southern California’s Santa Ana winds and northern California’s Diablo winds typically occur in November and December, as they historically have, Gershunov notes.
However, the seasonal conditions that precede these westward wind events have become extremely erratic. Heatwaves have intensified, and variability in precipitation has increased.
“It’s gotten really wild, from super wet years to super dry years,” Gershunov says.
Increasingly, the first of the season’s rains arrive weeks later than the historical average. This, combined with high autumn temperatures, creates prime fire conditions exactly when warm winds are gusting across the Bay Area — November, December, and even January.
“The fuels are drier longer, into the peak of the wind season,” Gershunov says, adding that climate models suggest this delayed start to the wet season “will become a trend.”
In a combustible and changing landscape, the state’s fire hazard mapping program helps guide responsible development — ostensibly, at least — by accurately reflecting where wildfires are most and least likely to occur.
“Building standards are tied to these maps,” McDougald explains. “And there are defensible space requirements tied to the fire hazard severity zones.”
While state law requires that officials update the maps periodically, it doesn’t specify how frequently updates must be made. Instead, it leaves that decision to the judgment of state fire officials. With the effects of climate change on California’s fire season becoming more noticeable each year, it’s only a matter of time before the next round of revisions are due.