A South Bay Levee Breaks Ground, And Records
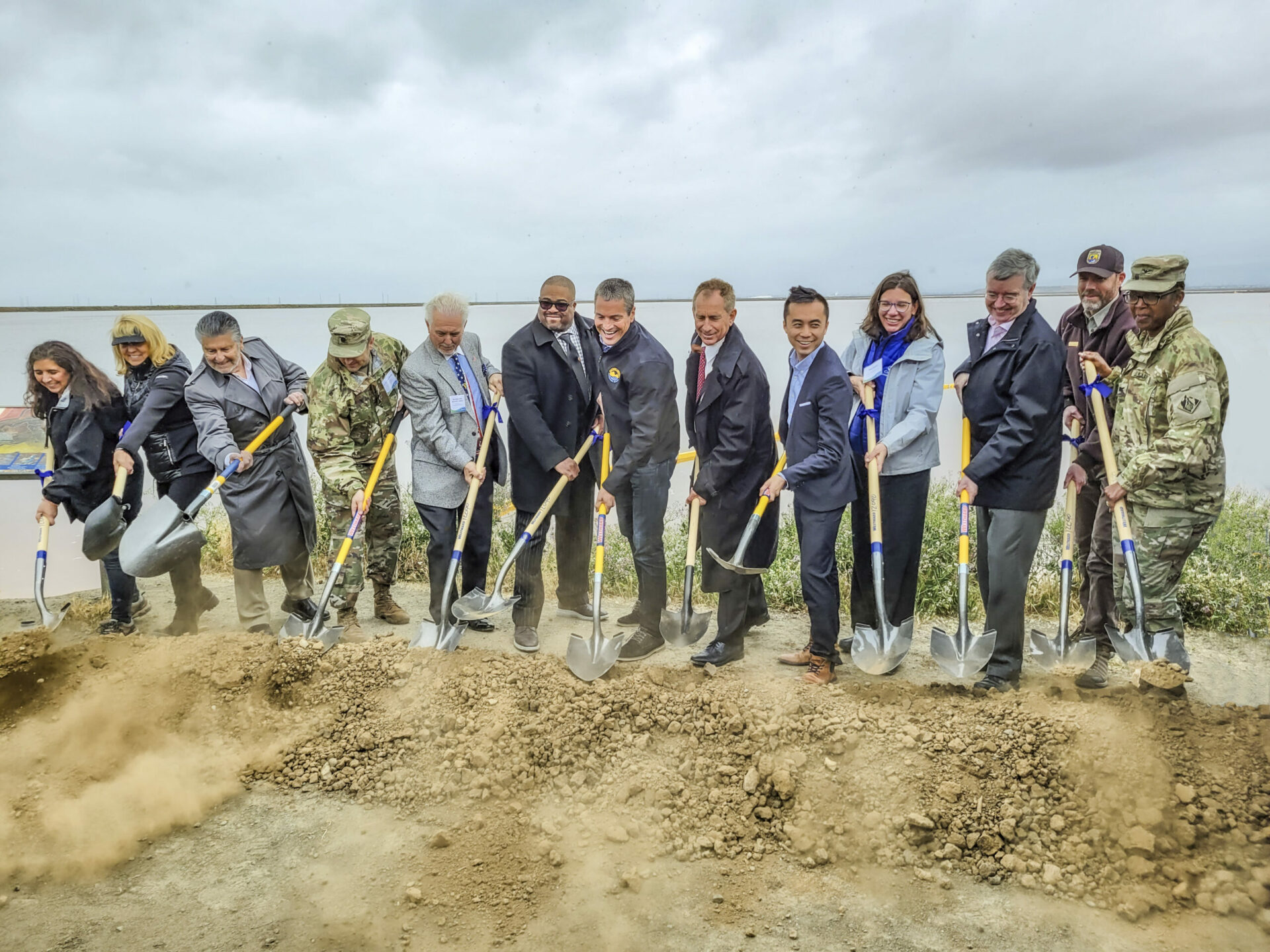
On a drizzly Thursday in April, dozens of reporters, government officials, military brass, conservationists, and bureaucrats gathered beside a weedy shoreline on the edge of San Jose to break ground on an effort worth hundreds of millions of dollars.
“We have a grave responsibility to take action, and what you see behind me is an example of that action,” declared Wade Crowfoot, the California Secretary for Natural Resources.
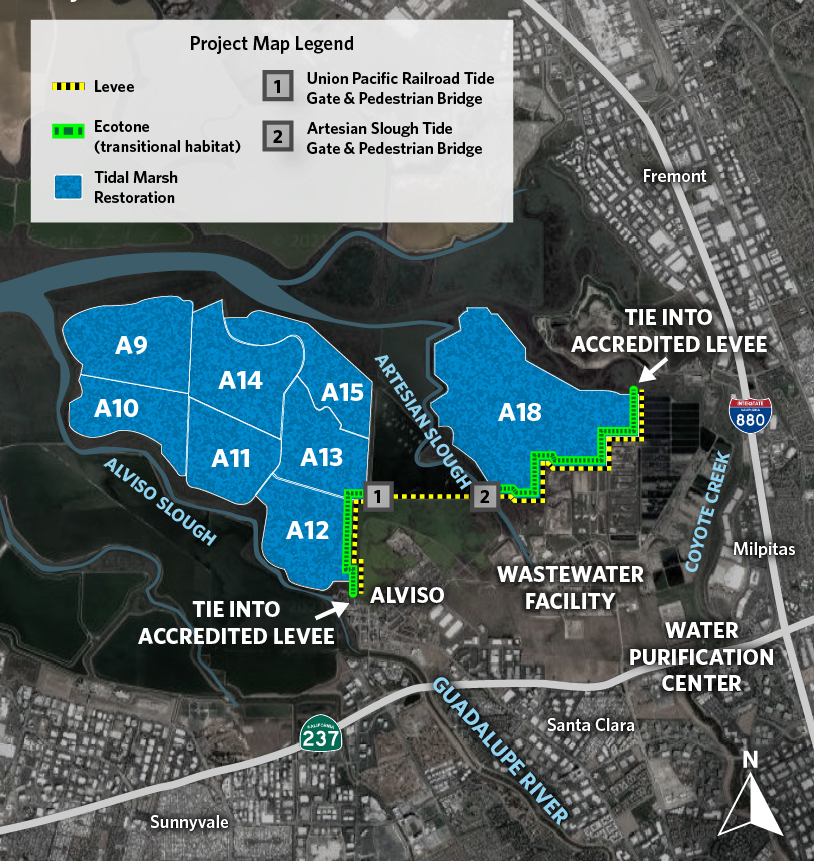
The humble surroundings belied the significance of the South San Francisco Bay Shoreline Project Groundbreaking. The project will include four miles of new levee and 2,900 acres of restored habitats, like tidal wetlands, to buffer the South Bay from rising seas. It is the culmination of nearly two decades worth of planning. The project is also the first in the nation in which the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers has incorporated sea-level rise into its planning and design, according to a Valley Water press release. And crucially, it’s distinct from piecemeal city-by-city levee improvements in that it aims to protect a vast swath of the South Bay at once.
Valley Water (formerly the Santa Clara Valley Water District) hosted the groundbreaking event alongside an alphabet soup of contributing organization members: the San Francisco Water District, Bay Conservation and Development Commission, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, California State Coastal Conservancy, and the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, alongside city, county, and state level elected officials. For many involved, the project’s broad popularity and multi-use benefits represent a best-case-scenario for sea level rise adaptation, and they’re impatient to see it working.
“We are at the crossroads and forefront of climate change,” said California Assemblymember Alex Lee. “It is very important that we continue to use natural solutions.” Nature-based infrastructure is the lynchpin of the South San Francisco Shoreline Project. Rather than walling off the most vulnerable areas from the Bay, the project will defend them from the encroaching sea with deployments of restored marshlands and sloping transition habitats along the levee.
These same defenses will also protect the San José-Santa Clara Regional Wastewater Facility, which serves over a million people. It is one of 36 wastewater treatment plants identified in California as vulnerable to sea level rise — 30 of which are in the Bay Area.
Other Recent Posts
Reforming Rules to Speed Adaptation
Bay Conservation and Development Commission to vote early this year on amendments designed to expedite approval of climate projects.
Warner Chabot Shifts Gears
After 11 years at the helm of the Bay Area’s leading science institute, its leader moves back into the zone of policy influence.
Is Brooklyn Basin Emblematic of Regional Development Vision?
The 64-acre waterfront development adds thousands of new housing units to one of the world’s most expensive places, but questions remain about its future.
Coordinate or Fall Short: The New Normal
Public officials and nonprofits say teaming up and pooling resources are vital strategies for success in a climate-changed world.
Pleasant Hill Gets Sustainable Street Improvements
An intersection redesign with safer bike lanes earned a national Complete Streets award, while sparking mixed reactions from drivers.
Six Months on the Community Reporting Beat
The magazine worked with four journalists in training from community colleges, and began building a stronger network in under covered communities.
Rio Vista Residents Talk Health and Air Quality
A Sustainable Solano community meeting dug into how gas wells, traffic, and other pollution sources affect local air and public health.
New Year Immerses Concord Residents in Flood Preparations
In Concord, winter rains and flood risks are pushed residents to prepare with sandbags, shifted commutes, and creek monitoring.
What You Need to Know About Artificial Turf
As the World Cup comes to the Bay Area, artificial turf is facing renewed scrutiny. Is it safe for players and the environment?
Threatened by Trump’s Policies, GreenLatinos Refuses to Back Down
National nonprofit GreenLatinos is advancing environmental equity and climate action amid immigration enforcement and policy rollbacks.
 Funding for the effort comes in part from Measure AA, a regional parcel tax for shoreline restoration work which Bay Area voters passed in June 2016. San Mateo County Supervisor Dave Pine, who is chair of the San Francisco Bay Restoration Authority charged with managing funds collected from the measure, said in his event speech that the Shoreline Levee project has been their number one priority for using those funds “from the very beginning, from the very design of Measure AA.” Although this large-scale levee project has years of frenetic work ahead to build the blueprint into reality, Pine and other officials are already envisioning future projects, to the tune of restoring 15,000 more acres of tidal wetlands across the Bay Area protecting and transforming its shoreline at once.
Funding for the effort comes in part from Measure AA, a regional parcel tax for shoreline restoration work which Bay Area voters passed in June 2016. San Mateo County Supervisor Dave Pine, who is chair of the San Francisco Bay Restoration Authority charged with managing funds collected from the measure, said in his event speech that the Shoreline Levee project has been their number one priority for using those funds “from the very beginning, from the very design of Measure AA.” Although this large-scale levee project has years of frenetic work ahead to build the blueprint into reality, Pine and other officials are already envisioning future projects, to the tune of restoring 15,000 more acres of tidal wetlands across the Bay Area protecting and transforming its shoreline at once.
California Assemblymember Alex Lee. Photo: USACE.