Global Study Finds Adaptation Progress Local Not Societal
Behind the public fanfare and declarations of international climate negotiations, like the COP26 conference that just ended in Glasgow, are thousands of researchers on the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) who toil for years to summarize the science on every aspect imaginable of climate change so policymakers have the best available facts to work from. But when hundreds of scientists working on the IPCC tried to summarize the research on how humans are adapting to climate change, they ran into a big problem: nobody was keeping track.
“A lot of times they’re mapping adaptation intentions or policies, like what do governments want to do?” explains Kripa Jagannathan, a UC Berkeley scientist. “But what is actually happening … wasn’t actually mapped out.”
The resulting Global Adaptation Mapping Initiative, or GAMI, ultimately roped in more than 120 scientists from across the world, over three years, to screen nearly 50,000 scientific papers published about adaptation to climate change within the last decade. The unfunded, international effort, which Jagannathan describes as “an absolutely crazy project,” was led by Lea Berrang-Ford at the University of Leeds in the U.K. and culminated in a massive summary published in October 2021.
Analyzing the 1,682 research papers that described adaptations already underway showed that societies across the world are starting to change to better confront the climate crisis. But “responses to climate change were largely local and incremental, with limited evidence of rapid, extensive, or transformative change,” wrote the research team. And they found “negligible evidence of risk reduction, the underlying aim of adaptation.”
For example, research about building seawalls or people migrating away from a high-risk region is already skewed towards papers about the best way to do it in theory, or considerations of ethics and policies; the seawalls and people in these articles are imaginary. But even among research focusing on real-life people and places trying to be more resilient to climate change, very little addresses whether it’s working. Are the seawalls really protecting people better? Are people migrating from their homes any safer for doing so?
Avery Hill, a Stanford researcher who assisted with the scientific grunt work of organizing some of the papers, says that while the results were unsurprising, they can be powerful if used to shape future research and policy.
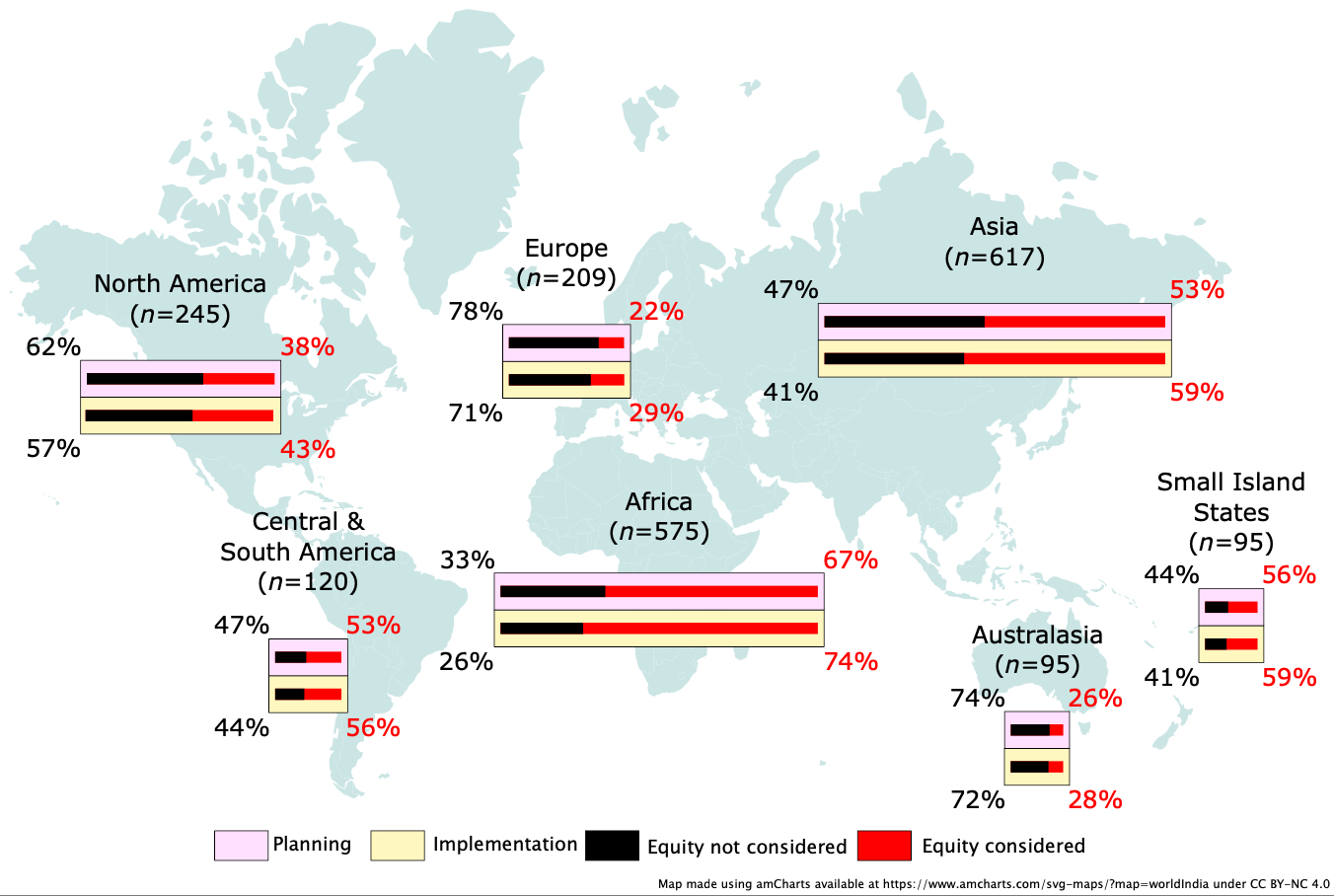
That’s already occurring to a degree. The mapping initiative inspired two dozen of the involved researchers, including Jagannathan, to launch another major analysis from the same database of scientific papers—this time, focused on equity in climate adaptation research. The team found that climate adaptation research in North America, Europe, and Australasia was unlikely to consider equity; the same went for adaptation articles about cities. The people most at risk of more extreme climate damages when equity is ignored include women, Indigenous groups, and low-income populations.
“People are responding to climate change because it’s affecting a lot of people, but it’s not enough,” says Hill. “And it’s not really happening at the right scale.”
Other Recent Posts
Agroecology Commons Weathers a Weird Winter and Political Storms
A year after our first Agroecology Commons visit, the El Sobrante farm has a new greenhouse foundation, thriving farmer training program, and some unexpected wildlife.
Finding Community at the Bay Area Climate Literacy Exchange
A third of our food supply goes to waste, and Bay Area students are learning how to fix it one school cafeteria at a time.
Easy Spring Vegetables for Small Gardens
Snap peas and Tokyo turnips are hardy, cool-season vegetables well-suited to Bay Area gardens. Here’s how to grow and cook them.
At Canticle Farm, Food and Community Are Prayer for a Better World
On a residential street in East Oakland’s Fruitvale neighborhood, a front yard becomes a food distribution network every Friday.
What Do Teens Think is Healthy Food?
Student reporting fellow Sachi Bansal asks three high school seniors in Fairfield about how they define healthy food, and what they think of the new food pyramid.
En Canticle Farm, la comida y la comunidad son las oraciones para un mundo mejor
Canticle Farm está reinventando el concepto de vecindario a través de la tierra compartida, la comida gratuita y la acogida radical.
En la granja agroecológica Agroecology Commons, las nutrias han vuelto
Un año tras nuestra primera visita a Agroecology Commons, la granja en El Sobrante tiene una nueva base para un invernadero, un próspero programa de entrenamiento para agricultores y una fauna inesperada.
Verduras de primavera fáciles de cultivar en jardines pequeños
Los chícharos dulces y los nabos japoneses son verduras resistentes al frío, ideales para los jardines del Área de la Bahía. Aquí te explicamos cómo cultivarlos y cocinarlos.
Entrenar futuros agricultores para que cultiven más que solo alimentos
En un colectivo del Área de la Bahía para agricultores BIPOC y queer, Brooke Porter y Alexa Levy luchan por construir, desde la tierra, un sistema alimentario inclusivo.
En comunidad durante el evento Bay Area Climate Literacy Exchange
Un tercio de nuestro suministro de alimentos se desperdicia, y estudiantes en el Área de la Bahía están aprendiendo cómo solucionarlo.