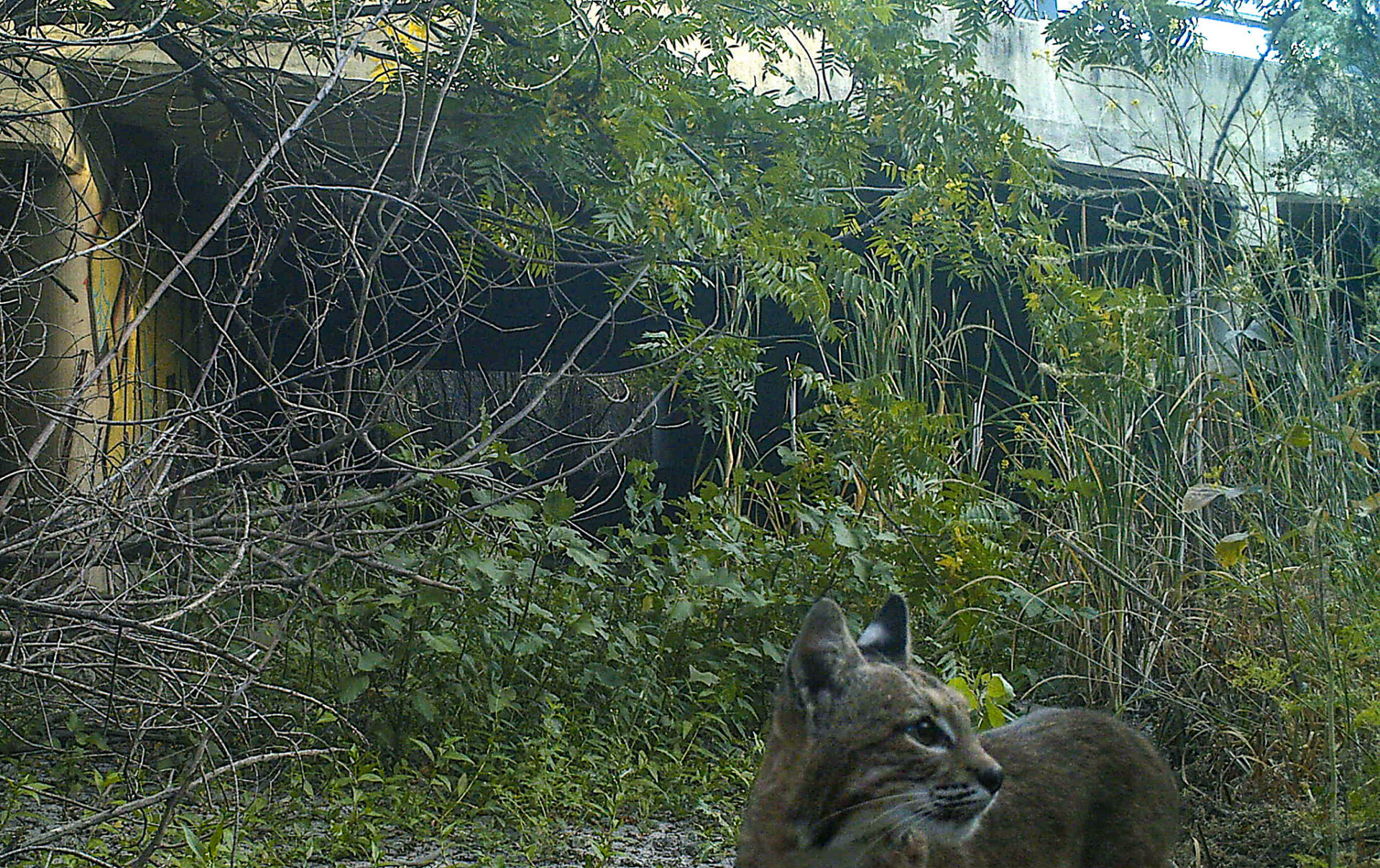
Ordering the Path to Wildlife Resilience
For nearly all organisms, connectivity is key. From small voyages to long, creatures must travel to find food, water, a mate, or a suitable patch of soil to put down roots. They need to avoid predators, wildfire, flood, and other hazards. This means they need wild pathways — corridors of trees, streams, meadows, or other habitat that allows them to move through a landscape increasingly fragmented by human alteration. And as climate change upends formerly stable patterns, wildlife’s need for corridors must also shift, often in complex ways, in order for each species and ecosystem to remain resilient.
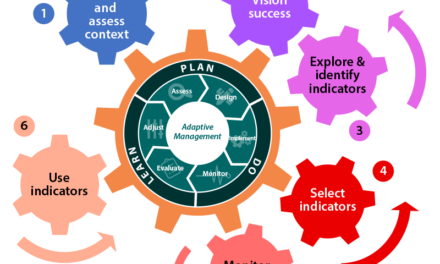
To help land managers respond to the increasing challenges of preserving useful wildlife corridors, the Association of Fish and Wildlife Agencies recently published a comprehensive collection of resources called the Connectivity and Climate Change Toolkit.
“It is useful to have compilations like this; for any individual organization or agency to start from scratch is a lot of work,” says Grant Ballard, chief science officer with the conservation non-profit Point Blue. “Some of the things identified I hadn’t seen before, and some are things we created that they used.”
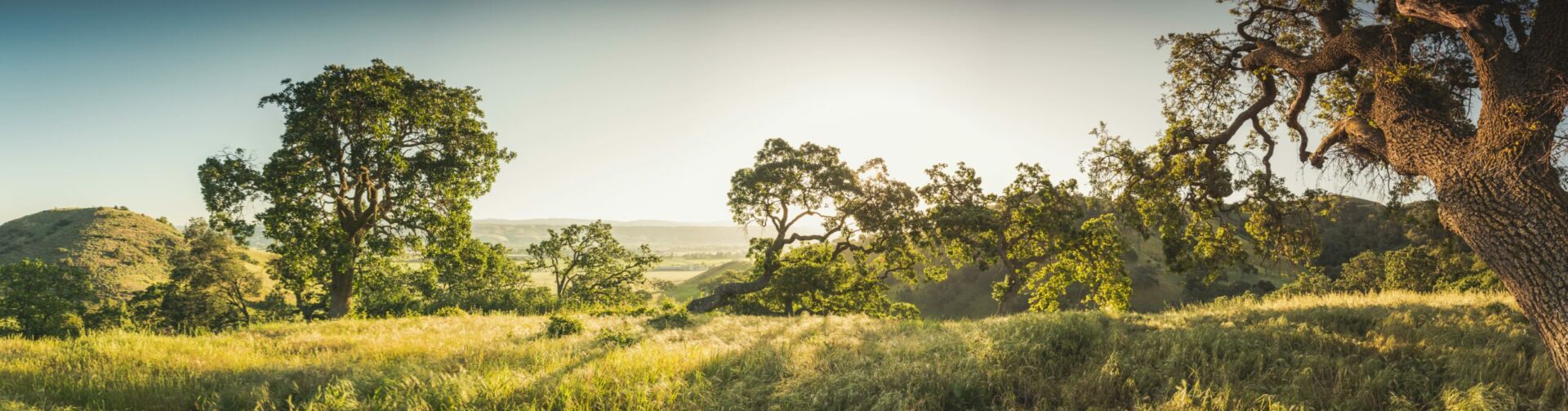

Local agencies recently set aside significant acreage in Santa Clara County’s Coyote Valley, a critical wildlife corridor under immense development pressure from urbanized San Jose.
Photo Courtesy: Lech Naumovich, SCVOSA.
While the need for wildlife corridors for everyday travel isn’t a new idea, planning for longer term shifts in the location and extent of habitats due to warming temperatures or increasing flooding is. “In light of climate change,” the report says, “connectivity is recognized for its potential to provide additional benefits for resiliency and adaptation strategies for fish and wildlife.”
The publication is broken up into categories such as Project Planning, Adaptation Strategies, and Considerations by Systems. Each category offers a summary of key resources, and a case study. From Forest Service guidance on road-stream crossing issues to software recommendations for how to plan fish-friendly culverts or predict connectivity, the toolkit has a diverse array of resources.
“This is the first time I have seen anything like this geared toward public agencies,” Ballard says. “It shows the intention to take a long view and do the work — so that is encouraging.”
Other Recent Posts
Assistant Editor Job Announcement
Part time freelance job opening with Bay Area climate resilience magazine.
Training 18 New Community Leaders in a Resilience Hot Spot
A June 7 event minted 18 new community leaders now better-equipped to care for Suisun City and Fairfield through pollution, heat, smoke, and high water.
Mayor Pushes Suisun City To Do Better
Mayor Alma Hernandez has devoted herself to preparing her community for a warming world.
The Path to a Just Transition for Benicia’s Refinery Workers
As Valero prepares to shutter its Benicia oil refinery, 400 jobs hang in the balance. Can California ensure a just transition for fossil fuel workers?
Ecologist Finds Art in Restoring Levees
In Sacramento, an artist-ecologist brings California’s native species to life – through art, and through fish-friendly levee restoration.
New Metrics on Hybrid Gray-Green Levees
UC Santa Cruz research project investigates how horizontal “living levees” can cut flood risk.
Community Editor Job Announcement
Part time freelance job opening with Bay Area climate resilience magazine.
Being Bike-Friendly is Gateway to Climate Advocacy
Four Bay Area cyclists push for better city infrastructure.
Can Colgan Creek Do It All? Santa Rosa Reimagines Flood Control
A restoration project blends old-school flood control with modern green infrastructure. Is this how California can manage runoff from future megastorms?
San Francisco Youth Explore Flood Risk on Home Turf
At the Shoreline Leadership Academy, high school students learn about sea level rise through hands-on tours and community projects.