National Toolkit Offers Steps & Metrics
Though averting the worst impacts of climate change and building local capacity for disaster response require immediate action, the best path forward is not always clear. As a scientist who has crossed over to policy analysis and development, I know that the process can be a slog. But when I reviewed the new Resilience Metrics toolkit, a vision of coherent, stakeholder-driven, place-based planning snapped into focus.
Dr. Susanne Moser and a team of colleagues created this toolkit by distilling lessons from ten years of previous projects, many in California. Moser is a veteran climate change and social science consultant with worldwide experience. The team asked themselves the deceptively difficult question, “What constitutes adaptation success?” Once this keystone is identified, everything else starts to fall into place.
Their product, the Resilience Metrics website, is like a food-for-thought buffet for project planners. This toolkit offers a set of questions designed to get a project on track and to help participants measure performance; it also offers facilitation aids, case studies, and links to videos, books, and research articles organized by topic.
Defining Success
Local planning processes may define “success” as being prepared to protect property and well-being in extreme events, or by developing a built environment that requires fewer resources to defend. Nature-based solutions that slow climate change impacts, such as marsh-building and prescribed fire, are possible “successes” as well.
Success might be measured by the avoidance of calamity, by the speed of recovery, or by who receives recovery assistance. “There is not one answer,” Moser said at a recent forum. “One person’s success might not be another person’s success. Maybe what you really want is an engaging and inclusive process.” By measuring outcomes, project leaders can identify both the parts that are working well and those that aren’t.
Metrics
The toolkit guides users to choose metrics that fit a project and produce meaningful information. Step one is a transparent stakeholder and community engagement process that aligns peoples’ priorities at the outset, incorporates diverse concerns, and encourages people to work together to achieve the outcomes they want. After developing an extensive array of potential metrics, users select final metrics according to the capacity of the team to carry them out, the ways they might be used, and whether existing monitoring efforts might meet the same need.
Coyotes remain one of the most adaptable species in urban areas. Photo courtesy Santa Clara Valley Open Space Authority.
Iterative Process
Over the past few years, the increasing intensity and frequency of disruptive weather has become undeniable. The best models for temperature anomalies, snowmelt, permafrost thaw, and other parameters rely on historical data. Now that weather is diverging from historical precedent, scientists are losing the ability to predict what’s happening in real time. For this reason, adaptive management is essential in climate resilience projects.
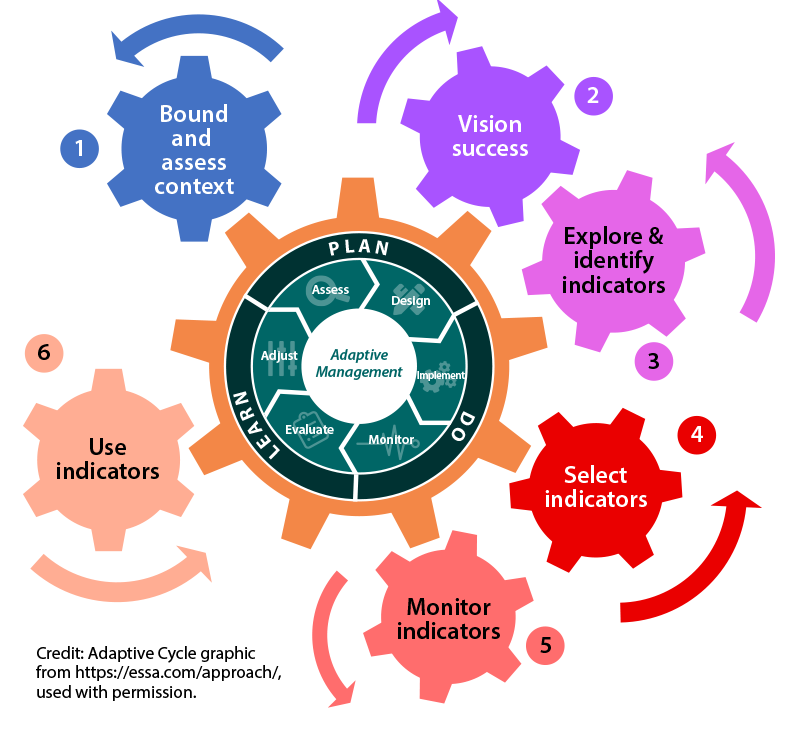
To help with adaptive management, the Resilience Metrics toolkit outlines four helpful steps: 1) assess project scope, context, needs, risks, and opportunities; 2) plan the project by setting goals and determining primary and alternative ways to reach them; 3) implement the project through decision-making, obtaining support (financial, political, and public), and taking action; and 4) learn from actions and experiences through monitoring and evaluation. From there, project managers can adjust practices as needed.
Closing
The essential — and daunting — task of facing the challenges of climate change lies ahead. Like many of us, I’ve personally felt the stress this can produce. As a scientist, I have watched with alarm as datasets diverge from historical norms. As a Californian, I have experienced increasingly intense and frequent wildfires, floods, and heat waves. The sooner communities throughout California and across the country start climate resilience projects, the better prepared they will be.
“This toolkit was designed to help people identify and use metrics to navigate the adaptation process and to make adaptation itself better,” says Moser.
Other Recent Posts
Building Sustainably with Mass Timber
This building method can help clear forests of smaller trees that burn easily while also reducing the carbon footprint of new homes and offices.
Hardscapes That Filter Rain
Heavy rain can overwhelm storm drains and pollute waterways, but materials like permeable pavements help filter runoff and prevent flooding.
The Gray-Green Alchemy of Baycrete
Baycrete is a nature-based hybrid of concrete, shell, and sand designed to attract oysters and create shallow water reefs in SF Bay.
Tools Tweak Beaver Dams
Humans find ways to co-exist with beavers, tweaking dams to prevent flooding and create more climate resilience.
Hopes and Fears for Sierra Snowpack
February’s drought and deluge confirms that uncertainty may be a given for California snowpack, western water supply, and wildfire risk.
Errands by E-Bike
Electric cargo bikes are climate-friendly car replacements for everyday activities, from taking the kids to school to grocery shopping.
A Rare Plant Tough Enough to Save the Future Bayshore
Sea-blite can thrive in adverse conditions, buffer shores from waves, hold sand and soil in place, and clamber up eroding cliffs.
ReaderBoard
Once a month we share reader announcements: jobs, events, reports, and more.
Reforming Rules to Speed Adaptation
Bay Conservation and Development Commission to vote early this year on amendments designed to expedite approval of climate projects.
Warner Chabot Shifts Gears
After 11 years at the helm of the Bay Area’s leading science institute, its leader moves back into the zone of policy influence.