Memo Distills Joint Approach to Flood Protection
With the region facing projected costs of at least $110 billion to protect its shores against rising waters, the failure to coordinate efforts on regional funding proposals can have serious consequences—an issue that was showcased recently when two local agencies both applied for the same multi-million-dollar federal grant program.
“This Federal agency only wanted one applicant from each region of the country,” says Allison Brooks of the Bay Area Regional Collaborative. “That’s the kind of miscommunication that can cost literally millions, where we end up not accessing the big dollars that we need.”
Avoiding similar snafus is one goal of a new Memorandum of Understanding approved on July 19 by seven regional and state agencies, committing them to work together to identify, prioritize and deliver high-priority, multi-benefit projects to reduce flood risks along the shoreline.
“This is a historic moment, when we lay out how we can use all our regulatory tools, all our expertise, all our strengths to work together to address the threat of sea level rise to our region,” said BARC chair and Berkeley mayor Jessie Arreguin at the July meeting.
The seven agencies include the Association of Bay Area Governments, the Bay Area Air Quality Management District, the California State Coastal Conservancy, CalTrans District 4, the Metropolitan Transportation Commission, the San Francisco Bay Conservation and Development Commission, and the San Francisco Bay Regional Water Quality Control Board.
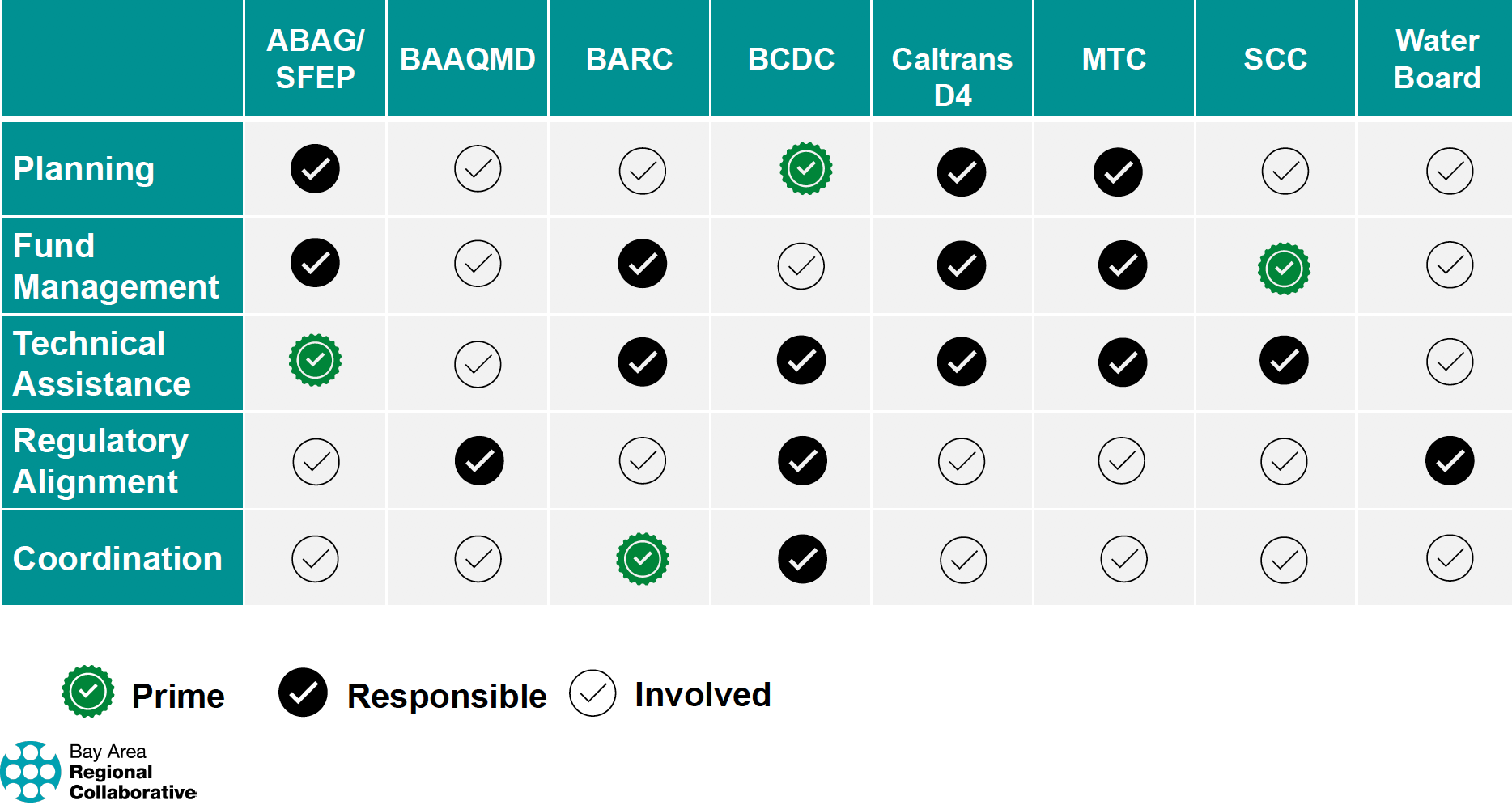
The MOU establishes the first coordinated regional strategy to fund and deliver the types of projects the Bay Area will need to protect vulnerable communities from the effects of climate change. It delineates the roles and responsibilities of each agency with regard to the different aspects of developing and executing adaptation projects. The agreement identifies these core functional areas as planning, fund management, technical assistance, regulatory alignment and coordination.
Roles and responsibilities for the seven agencies as laid out in the new MOU. Source: BARC
Other Recent Posts
Building Sustainably with Mass Timber
This building method can help clear forests of smaller trees that burn easily while also reducing the carbon footprint of new homes and offices.
Hardscapes That Filter Rain
Heavy rain can overwhelm storm drains and pollute waterways, but materials like permeable pavements help filter runoff and prevent flooding.
The Gray-Green Alchemy of Baycrete
Baycrete is a nature-based hybrid of concrete, shell, and sand designed to attract oysters and create shallow water reefs in SF Bay.
Tools Tweak Beaver Dams
Humans find ways to co-exist with beavers, tweaking dams to prevent flooding and create more climate resilience.
Hopes and Fears for Sierra Snowpack
February’s drought and deluge confirms that uncertainty may be a given for California snowpack, western water supply, and wildfire risk.
Errands by E-Bike
Electric cargo bikes are climate-friendly car replacements for everyday activities, from taking the kids to school to grocery shopping.
A Rare Plant Tough Enough to Save the Future Bayshore
Sea-blite can thrive in adverse conditions, buffer shores from waves, hold sand and soil in place, and clamber up eroding cliffs.
ReaderBoard
Once a month we share reader announcements: jobs, events, reports, and more.
Reforming Rules to Speed Adaptation
Bay Conservation and Development Commission to vote early this year on amendments designed to expedite approval of climate projects.
Warner Chabot Shifts Gears
After 11 years at the helm of the Bay Area’s leading science institute, its leader moves back into the zone of policy influence.
“We know that climate change is a huge regional problem that needs regional solutions and regional coordination from the leaders of the Bay Area agencies,” says SF Water Board chair Eileen White. “Instead of competing for different resources, tackling the same problems, we will be much more effective in addressing climate change by working together. We can achieve more and be strategic about what funding we want to pursue.”
The MOU’s objectives include identifying priority projects through a process that incorporates local sea level rise adaptation plans, supporting multi-jurisdiction partnerships, and helping cities, counties and special districts plan and fund climate adaptation projects.
Len Materman of the San Mateo County Flood and Sea Level Rise Resiliency District says his agency is “grateful to the State and regional agencies that developed the MOU for understanding the urgency of planning and building resilience to the impacts of climate change.”
“We need unprecedented coordination to prioritize flood risk management projects in the places that need them most,” says ABAG Executive board Vice President Bella Ramos. “We must accelerate our pace and plan at a scale commensurate with the risk. This MOU is an important step.”