Pricing Climate Risk
Economics has been called the dismal science. That label might seem to apply in spades to a novel sub-specialty: the art of pricing the risks of climate change, a concern not least to the insurance industry.
To get the basics, you could do worse than to talk to Dag Lohmann. Physics at the U. of Göttingen in Germany. Post-doc in civil engineering at Princeton. Six years with the National Weather Service. Almost eight with a leading risk modeling company, RMS. Ten, and counting, with his own Berkeley firm, KatRisk LLC, focused on various kinds of flooding. Oddly, at the end of that conversation, you might come out feeling just a little less dismal.
Insurance shifts costs from individuals to groups. It also shifts costs from after an untoward event to before. Your auto insurance shares your risk with millions of other drivers, giving each a small load now to protect each against a possibly crushing burden later. Flood and fire insurance, ideally, should work the same way; but the creeping change in climate is changing their arithmetic.
Just how much, and with what financial consequences, is Dag Lohmann’s province. His team knows and applies the latest science. “We’re the middleman between scientists and insurers,” he says. “We rely on research and data from universities and government labs, but do our own simulations.” Lohmann can, for instance, quantify the creep in storm surge losses caused by sea level rise. In the U.S. these are climbing by about half a percent per year, he says, a rate that is sure to increase.
The news is less bad for inland flooding and those seeking insurance against it. Premiums vary wildly nationwide. Some properties should be paying more than they do now for their policies, but many should actually be paying less. Subtle assessments can bring fairer pricing; they can also help in the design of protective measures. Financial players of several kinds may find it prudent to invest in prevention, reducing the cost of cure.
Like big fleas feasting on littler fleas, insurance companies also buy insurance, to cover them against the occasional catastrophic loss; specialized re-insurance companies, with names like Swiss RE and Munich RE, exist to fill this role. A further wrinkle has recently emerged: the packaging of these reinsurance policies as bonds sold to investors—what the trade calls securitization. People with money buy these “catastrophe bonds,” (cat bonds for short), taking the risk of the occasional bath (a risk to be assessed by analysts like Lohmann’s) in return for considerable annual profit.
Other Recent Posts
Tools Tweak Beaver Dams
After witnessing fire disasters in neighboring counties, Marin formed a unique fire prevention authority and taxpayers funded it. Thirty projects and three years later, the county is clearer of undergrowth.
Reforming Rules to Speed Adaptation
Bay Conservation and Development Commission to vote early this year on amendments designed to expedite approval of climate projects.
Warner Chabot Shifts Gears
After 11 years at the helm of the Bay Area’s leading science institute, its leader moves back into the zone of policy influence.
Is Brooklyn Basin Emblematic of Regional Development Vision?
The 64-acre waterfront development adds thousands of new housing units to one of the world’s most expensive places, but questions remain about its future.
Coordinate or Fall Short: The New Normal
Public officials and nonprofits say teaming up and pooling resources are vital strategies for success in a climate-changed world.
Pleasant Hill Gets Sustainable Street Improvements
An intersection redesign with safer bike lanes earned a national Complete Streets award, while sparking mixed reactions from drivers.
Six Months on the Community Reporting Beat
The magazine worked with four journalists in training from community colleges, and began building a stronger network in under covered communities.
Rio Vista Residents Talk Health and Air Quality
A Sustainable Solano community meeting dug into how gas wells, traffic, and other pollution sources affect local air and public health.
New Year Immerses Concord Residents in Flood Preparations
In Concord, winter rains and flood risks are pushed residents to prepare with sandbags, shifted commutes, and creek monitoring.
What You Need to Know About Artificial Turf
As the World Cup comes to the Bay Area, artificial turf is facing renewed scrutiny. Is it safe for players and the environment?
When Hurricane Katrina struck the Gulf Coast in 2005, a specialized fund called Kamp Re took a heavy hit and dissolved. Its investors lost about three quarters of their money. But Kamp Re did pay its insurance company clients, and those companies in turn paid the individual policy holders. In a sense, the system can be said to have worked, shifting cost from those least capable to those most capable of paying.
Katrina dramatized the need for better risk assessment, but it did not dampen the rise of “cat bonds.” The National Flood Insurance Program (the nation’s largest single-line insurance program) issues quantities of these, and KatRisk is right there, acting as “calculation agent” for the last five rounds of bonds. The company has thus helped shift more than $1 billion in hurricane risk from NFIP to the capital markets, Lohmann says.
In California, far from hurricane country, the flood risks tend to be more chronic than dire. The typical problem here is different: too few of us can find affordable insurance, making post-disaster recovery hard. The community benefit insurance concept (see “Overhauling Insurance” below) is a possible fix, applicable also to fire. Earthquakes are another matter, where the catastrophe bond concept might apply.
So here is an industry, not known for altruism, doing its part to wrestle with huge societal problems. This is surely encouraging, up to a point. But as climate weirdness mounts, there will be more and more situations where the insurance model is simply obsolete. “Over what time frames,” Lohmann asks, “might insurance not be possible anymore in parts of Louisiana or Florida?”
The story has its dismal side, after all.
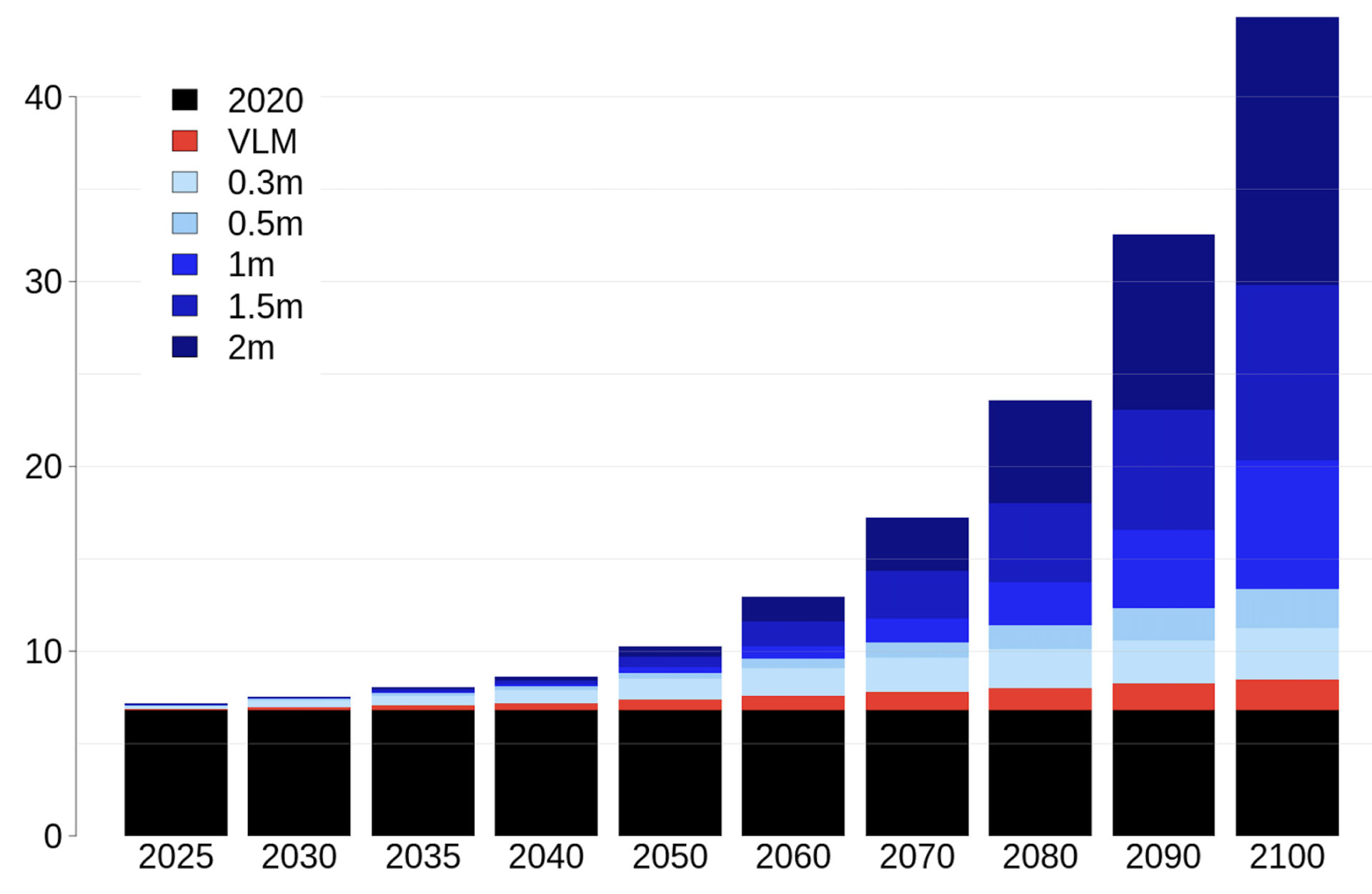
Average annual loss to storm surge from Atlantic hurricanes in billions of dollars under different global sea level rise scenarios in meters by the year 2100. The analysis translates government data (the latest NOAA sea level rise projections) into financial losses. (VLM = vertical land movement, largely from Louisiana and Florida sinking.) Source: KatRisk.