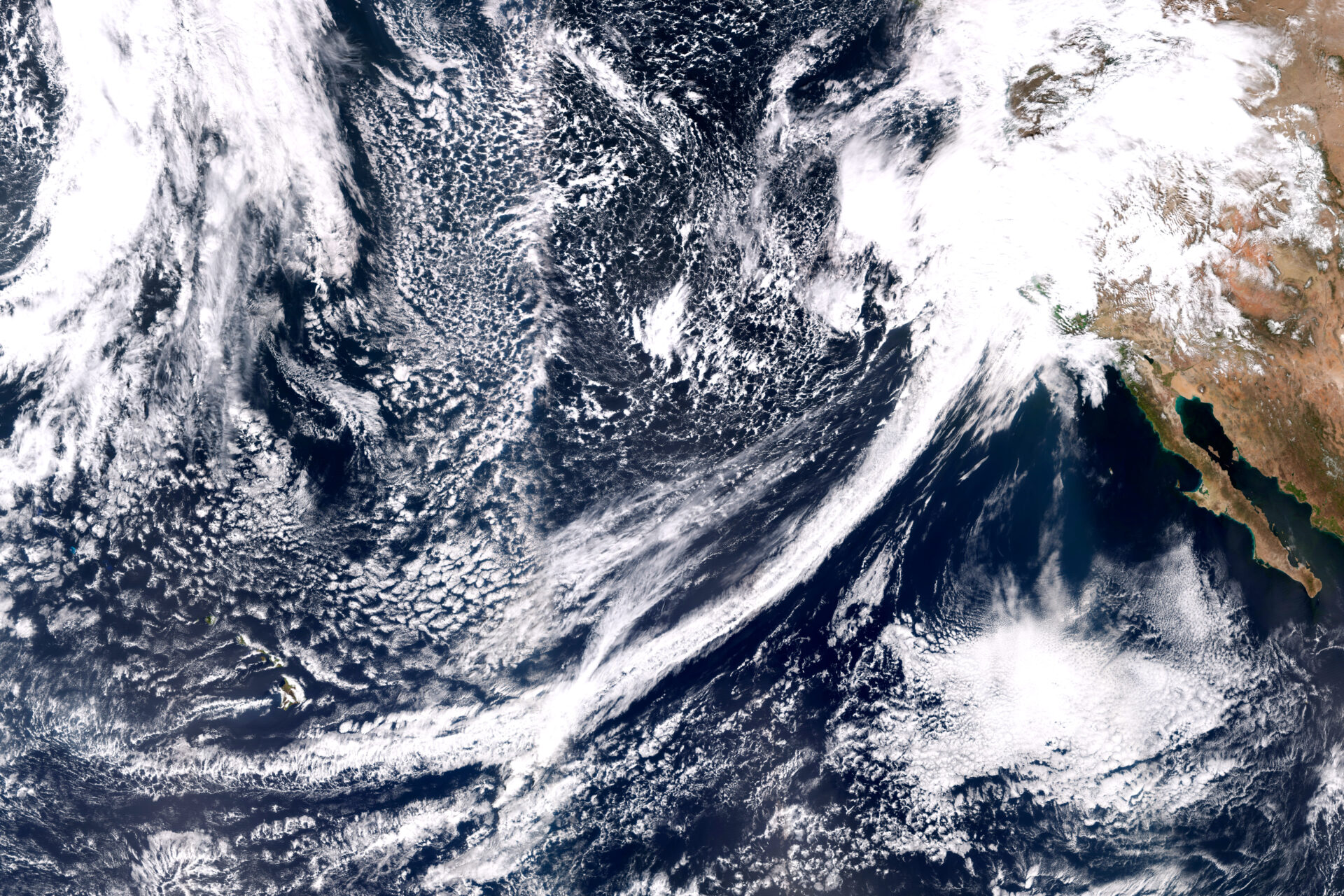
How Rivers in the Sky Travel Across the Ocean
Winter in California is a time of promise and peril. We’re desperate for rain, only not too much please. Our fate swings from drought to floods, depending largely on whether or not we get rainstorms called atmospheric rivers. These ribbons of extraordinarily wet air shoot across the Pacific Ocean, dropping the moisture they carry upon landfall.
The Bay Area’s latest “wet” season began with the bang of a record-breaking atmospheric river in late October but then fizzled out. These storms have been so scarce in the last few months that the state is facing a third year of deepening drought.
Atmospheric rivers typically begin over oceans in the tropics, where it’s so warm that water evaporates readily, filling the air with moisture. Then all it takes to start an atmospheric river is a storm called an extratropical cyclone, which spins over the ocean and sweeps up the wet air.
“Atmospheric rivers are seeded by convection storms that move water vapor from the surface to a couple of kilometers high,” says Alan Rhoades, a hydroclimate scientist at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory.
Atmospheric rivers that form over the Pacific Ocean are then launched and propelled toward the West Coast by strong winds. “You need a driver like a low-level jet stream,” says Zhenhai Zhang, an atmospheric scientist at Scripps Institution of Oceanography. “The jet carries the moisture and moves fast in a narrow corridor.”
This airborne stream of water vapor then traverses a series of low and high pressure regions that are strung across the ocean. These regions set the path of the atmospheric river, which can be so long that it extends halfway across the Pacific. “A low grabs the water vapor and moves it northward, and a high then steers it toward the West Coast,” Rhoades says.
He likens this process to a conveyor belt, where the low and high pressure systems are like rollers that direct the atmospheric river. Another way to look at this process is that the low and high pressure areas are like the pegs of an enormous pinball machine, guiding and redirecting the flow of the atmospheric river and so shaping its trajectory toward land.
Other Recent Posts
Building Sustainably with Mass Timber
This building method can help clear forests of smaller trees that burn easily while also reducing the carbon footprint of new homes and offices.
Hardscapes That Filter Rain
Heavy rain can overwhelm storm drains and pollute waterways, but materials like permeable pavements help filter runoff and prevent flooding.
The Gray-Green Alchemy of Baycrete
Baycrete is a nature-based hybrid of concrete, shell, and sand designed to attract oysters and create shallow water reefs in SF Bay.
Tools Tweak Beaver Dams
Humans find ways to co-exist with beavers, tweaking dams to prevent flooding and create more climate resilience.
Hopes and Fears for Sierra Snowpack
February’s drought and deluge confirms that uncertainty may be a given for California snowpack, western water supply, and wildfire risk.
Errands by E-Bike
Electric cargo bikes are climate-friendly car replacements for everyday activities, from taking the kids to school to grocery shopping.
A Rare Plant Tough Enough to Save the Future Bayshore
Sea-blite can thrive in adverse conditions, buffer shores from waves, hold sand and soil in place, and clamber up eroding cliffs.
ReaderBoard
Once a month we share reader announcements: jobs, events, reports, and more.
Reforming Rules to Speed Adaptation
Bay Conservation and Development Commission to vote early this year on amendments designed to expedite approval of climate projects.
Warner Chabot Shifts Gears
After 11 years at the helm of the Bay Area’s leading science institute, its leader moves back into the zone of policy influence.
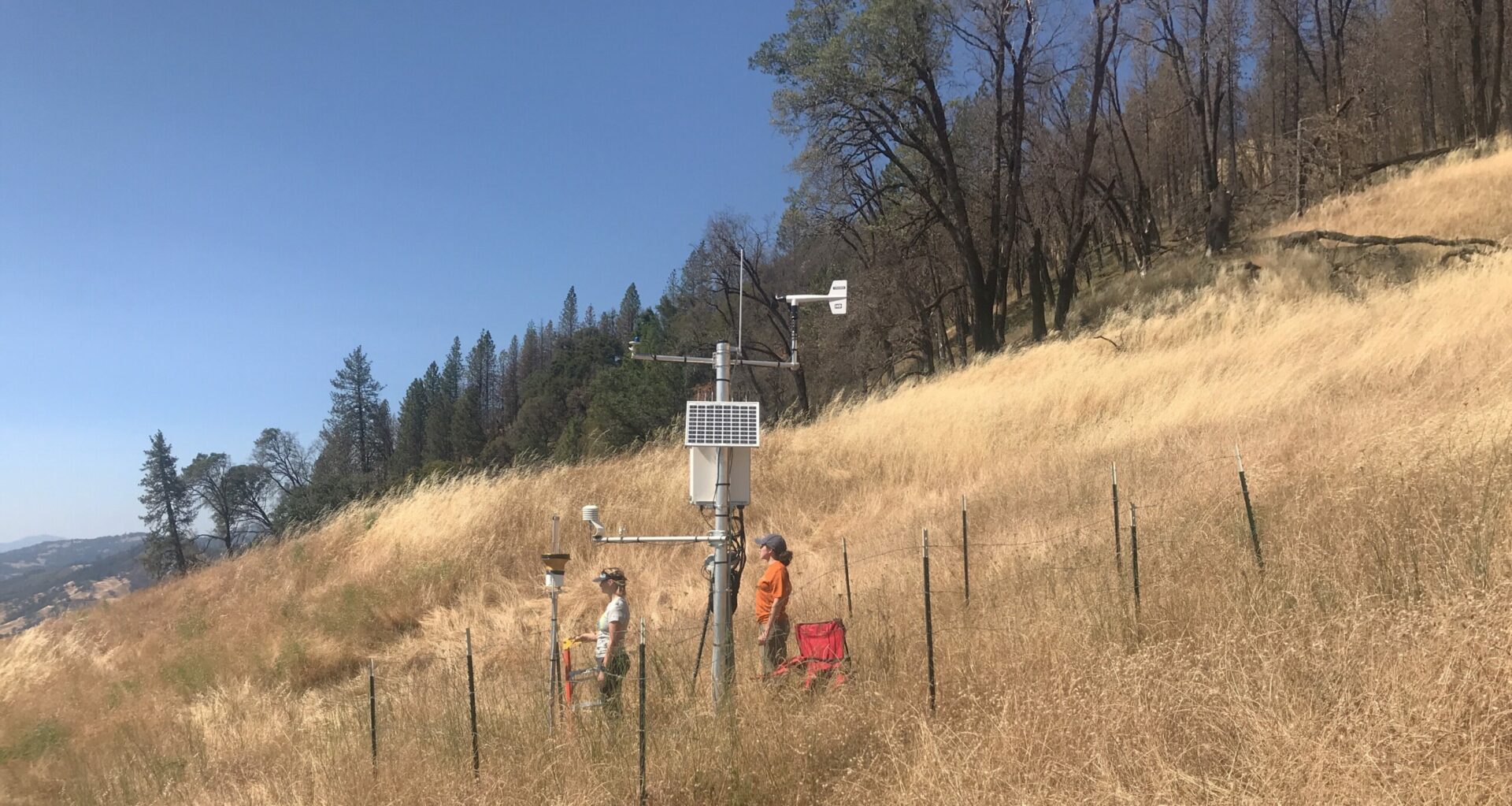
Instruments on this Sonoma County ridge measure precipitation, temperature, humidity, winds, barometric pressure, and more. Scientists use the data to connect the hydrology of the Russian River watershed to atmospheric river forecasts. Photo: Scripps, UCSD.
That trajectory is hard to predict, however. “Atmospheric rivers are often called whips or hoses because their path can shift in different directions,” Rhoades says. This is partly because these storms depend on wind, which changes from hour to hour. Atmospheric river speeds are difficult to pin down but may vary from 20 to 100 kilometers per hour.
And while the path can look fairly smooth at a global scale, up close it’s a different story. “At a small scale, it’s challenging to predict the exact path of an atmospheric river,” Zhang says, adding that an atmospheric river’s size, shape and intensity are also in flux.
Taken together, all this variability makes it hard to know exactly how strong an atmospheric river will be and exactly where it will make landfall. Another complication is that atmospheric rivers can be just a few hundred kilometers across. This is very close to the uncertainty in predictions of where they will hit, which can be off by a couple hundred kilometers. “That’s the difference between landfall in Los Angeles or in San Diego,” Zhang notes.